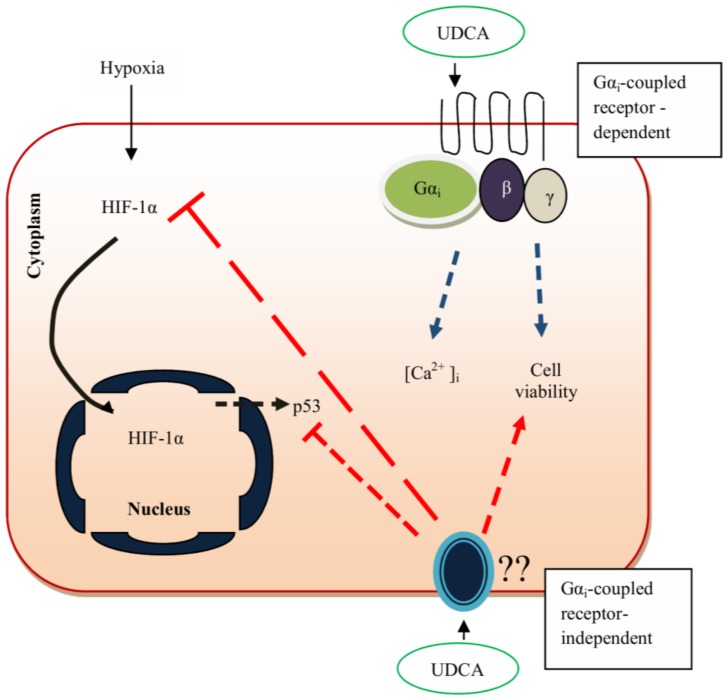
Figure 3.
Proposed mechanisms for UDCA cardioprotection in maintaining normal [Ca2+]i and HIF-1α level. Binding of UDCA to PTX-sensitive receptor partially improves cell survival. However, PTX does not block the effect of UDCA on [Ca2+]i, HIF-1α translocation, and p53 protein expression against hypoxia. Cell viability is partially inhibited by PTX; dual pathway is suggested to be involved (Gαi-coupled receptor-dependent and -independent pathways). Blue arrow, Gαi-coupled receptor-dependent pathways; red arrow, Gαi-coupled receptor-independent pathways. (UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid; Gαi, G-alpha; ẞ, G-beta; γ, G-gamma; Hif-1 alpha, hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha; [Ca2+]i, intracellular calcium; p53, cellular tumor antigen p53).