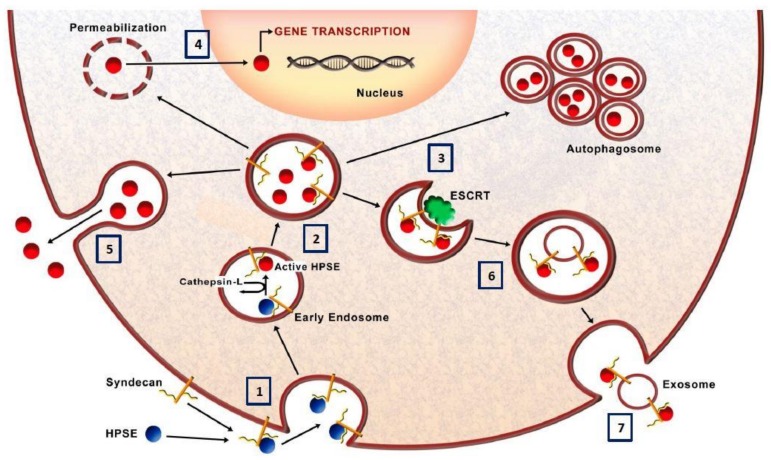
Figure 1.
Schematic model of heparanase trafficking. (1) The inactive pro-HPSE in the extracellular spaces interacts with HS-proteoglycans such as syndecan-1 and the complex is endocytosed. (2) The fusion of endosomes with lysosomes, with the consequent acidification, induces the activation of HPSE exerted by the cleavage by cathepsin-l. (3) Here HPSE participates in the formation of autophagosome and thus controls the basal levels of autophagy. (4) HPSE can translocate into the nucleus where it can modulate gene transcription or (5) it can be secreted in the extracellular space. (6) Moreover, HPSE modulates the formation and the release of exosomes and (7) active HPSE is also released and anchored to syndecan on exosome surfaces. Collectively, by regulating autophagy and the production of exosomes, HPSE modulate several mechanisms which characterize cancer chemoresistance [62,63].