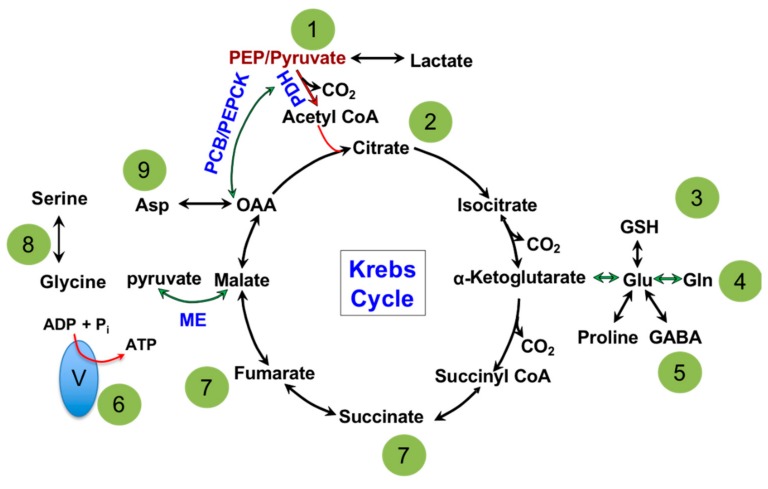
Figure 1.
Major pathways and metabolite exchange that take place in the mitochondria. 1: Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis connects to the mitochondria by phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), pyruvate and lactate. 2: Fatty acid biosynthesis and oxidation utilize citrate and acetyl-CoA as metabolic intermediates. 3: Glutathione (GSH) is produced in the mitochondria from glutamate, which maintains cellular redox balance. 4: Protein biosynthesis uses de novo synthesized amino acids from the mitochondria. 5 Neurotransmitter biosynthesis (proline and GABA) partially takes place in the mitochondria then continues in the cytosol. 6: Electron Transport Chain subunits I-V make up the Oxidative Phosphorylation pathway and are located on the inner mitochondrial membrane and use reducing equivalents, NADH and FADH2, as electron sources. Electrons move through the subunits from I or II to IV, which creates a proton gradient in the process. The proton gradient is used by subunit V to generate ATP. 7: Fumarate and succinate are exported to the cytosol as enzyme co-factors. 8: 1-carbon metabolism supplies carbon for purine nucleotide biosynthesis and methylation of proteins and DNA. 9: Aspartate (Asp) supports pyrimidine ring biosynthesis. →: Canonical oxidative pathway. →: Anaplerotic pathway. Pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH); pyruvate carboxylase (PCB); phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK); malic enzyme (ME); gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).