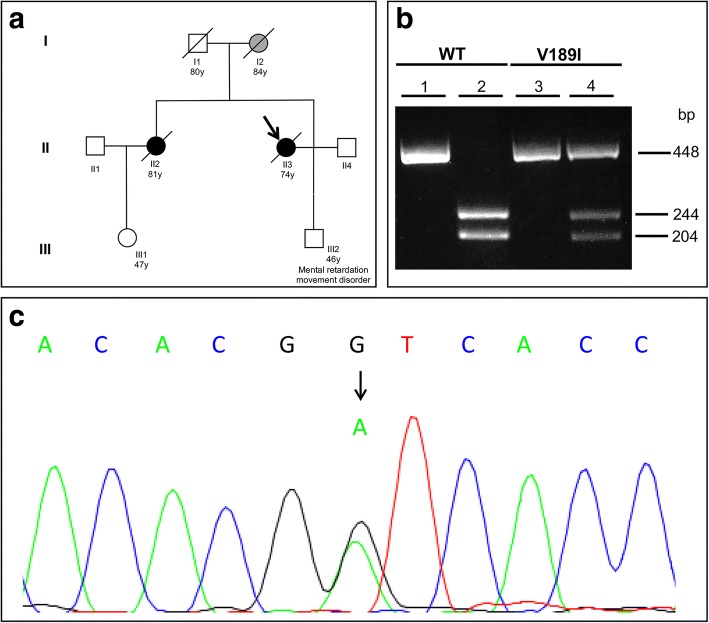
Fig. 2.
Genetic studies. a: Pedigree of family of Cases 1 and 2. The proband is marked by arrow, grey symbols denote family members affected by rapidly progressive dementia, black symbols indicate family members with CJD, white symbols denote unaffected members. Crossing lines refer to deceased subjects. b: Analysis of PRNP gene by restriction fragment length polymorphism. A 448 bp region was amplified by PCR from a control subject (WT, lane 1) and a mutated heterozygous carrier (V189I, lane 3) . Digestion of PCR product by BstEII generated two fragments (244 and 204 bp) in the WT subject (lane 2). The presence of the mutation abolished the restriction site. So, a 448 bp fragment (corresponding to the mutated allele) and two 244 and 204 bp fragments (corresponding to the WT allele) were observed, as expected, in the V189I heterozygous carrier (lane 4). c: Sequence chromatogram of a subject carrying the heterozygous V189I mutation