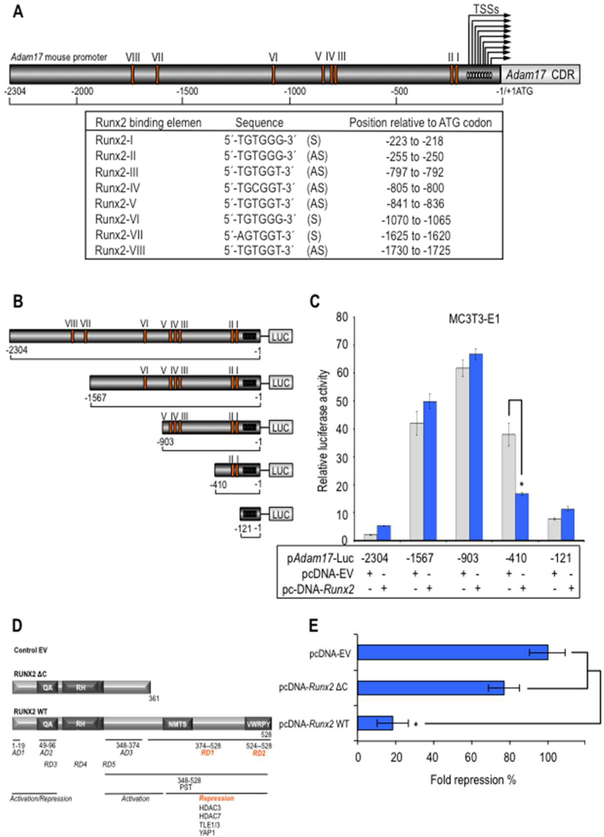
Figure 3. Adam17 promoter has a proximal region containing RUNX2 binding sites supporting transcriptional repression.
Adam17 gene promoter from mouse was analyzed for the presence of the genome-wide consensus Runx motif (5’-[A/C]CC[A/T/G]C[A/T/G]-3’) previously established for us (van der Deen et al., 2012) (A). S and AS indicated sense- and antisense-stranded DNA. Arrows indicated transcription start sites (TSS) (−161 to −55, relative to ATG codon). MC3T3–E1 cells were transfected with either a luciferase reporter gene under transcriptional control of the promoter region of mouse Adam17 (pAdam17 2.3-Kb) or with a series of deletion mutants spanning the mouse Adam17 gene promoter that overexpress will-type Runx2 or empty vector control pcDNA 3.1 (EV) for Runx2 expression construct (B and C). Effect of will type Runx2 (Runx2 WT) or deletion mutant Runx2 1–361 (Runx2 ΔC) expression or empty vector control pcDNA 3.1 (EV) on 0.4-Kb Adam17 proximal promoter was also determined by a luciferase activity assay (D and E). The promoter activity was determined by a luciferase activity assay after 24 h of transient transfection and normalized by cotransfection with Renilla luciferase. All data are presented as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. *P<0.05.