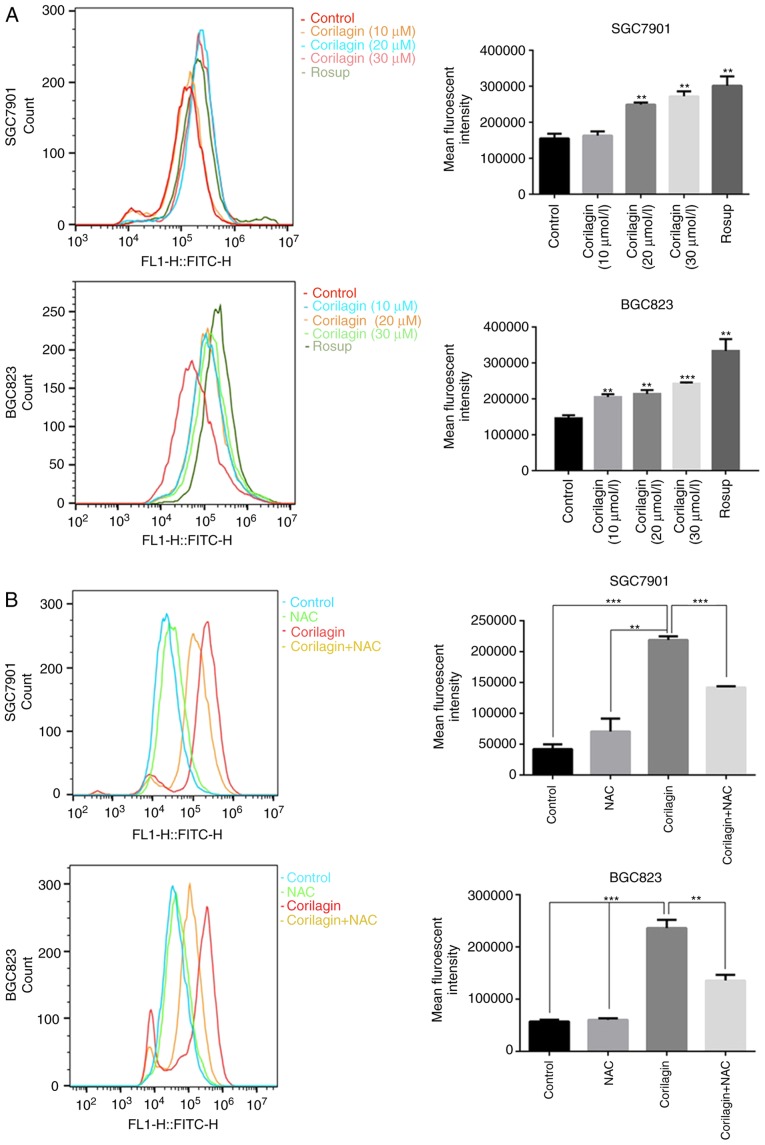
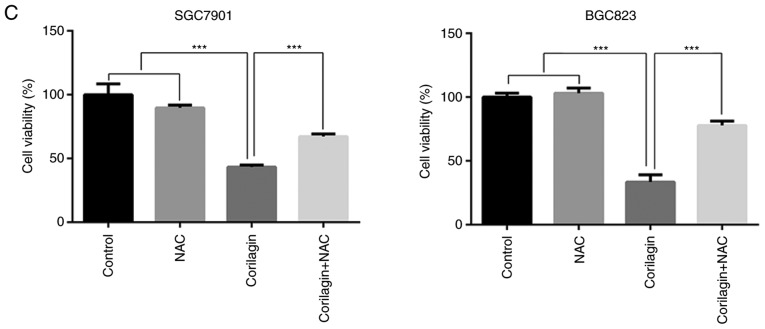
Figure 6.
Corilagin triggers ROS generation in gastric cancer cells. (A) Cells were treated with corilagin at various concentrations (0, 10, 20 and 30 µM) for 24 h and then labeled with DCFH-DA (10 µM). ROS production were measured by flow cytometry (Rosup as positive control). (B) Pre-treatment with NAC (5 µM) for 2 h and then incubated with corilagin (30 µM) for 24 h. Cells were stained with DCFH-DA (10 µM) and then ROS levels were determined using flow cytometry. (C) Cells were pretreated with NAC (5 µM) and then exposed to corilagin (30 µM) for 24 h. Following treatment, the cell viabilities were detected using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenytetrazolium bromide assay. The data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation (n=3) of three replicate experiments. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs. control group (detected using Student's t-test). ROS, reactive oxygen species; NAC, N-acetyl-L-cysteine.