Figure 3.
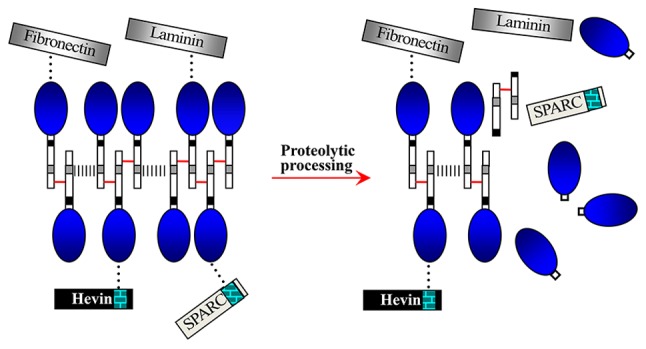
Interactions of myocilin with extracellular matrix proteins (laminin and fibronectin) and matricellular proteins (SPARC and hevin) (34). Homoaggregates of myocilin monomers covalently interact through disulfide bonds (short red lines) within LZ (12). Myocilin complexes interact by noncovalent bonds (grey dashed lines) in N-terminus (rectangle linked to the blue oval). Full-length myocilins non-covalently (black dots) interact with the extracellular calcium binding domains (brick pattern) of SPARC and hevin through OLF (blue oval). Interacting fashion of myocilin with laminin and fibronectin could be similar to that of SPARC and hevin. SPARC, secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine; LZ, leucine zippers; OLF, olfactomedin.
