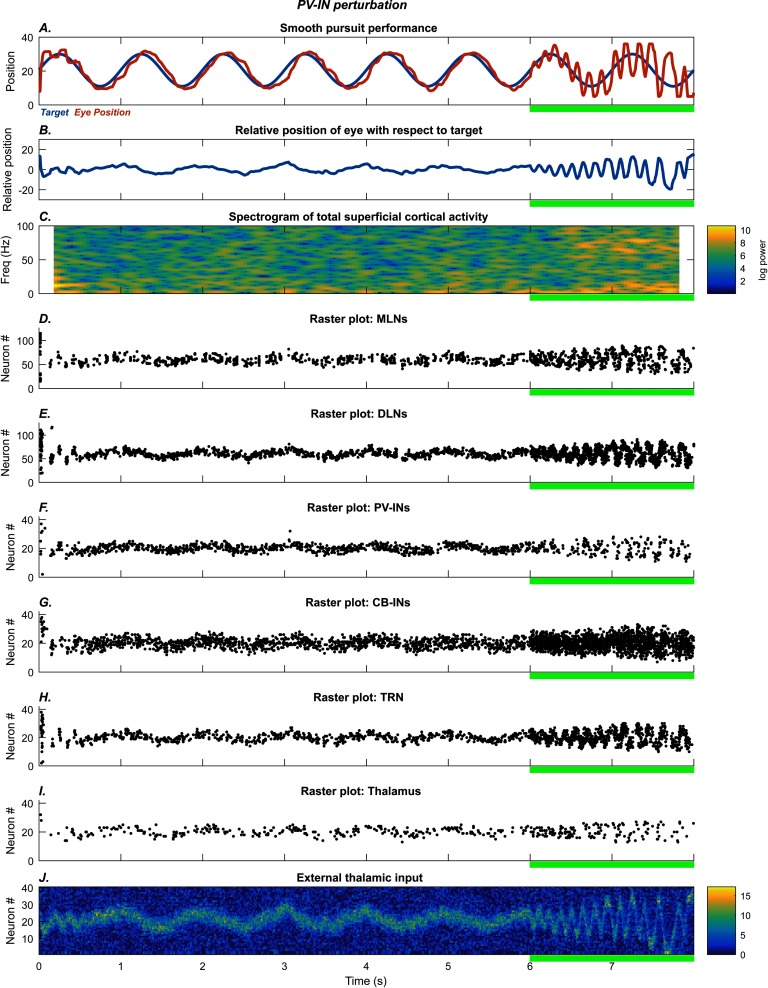
Figure 2. .
PV-IN perturbation: smooth pursuit task. The system quickly settles on accurate smooth pursuit of the stimulus. After the 6 s mark (green bar), glutamatergic NMDA conductance on the PV-INs is reduced, leading to increased variability in eye movement. The subplots show the time evolution of model behavior (A–B) and model neural activities (C–I) as well as external thalamic input (J). A) Horizontal position of the model eye (red trace) and the target (blue trace) in absolute coordinates. B) Relative position of the eye with respect to the target. C) Spectrogram of total middle-layer cortical activity. D–I) Raster plots show spiking activity in the model neurons. J) External thalamic input.