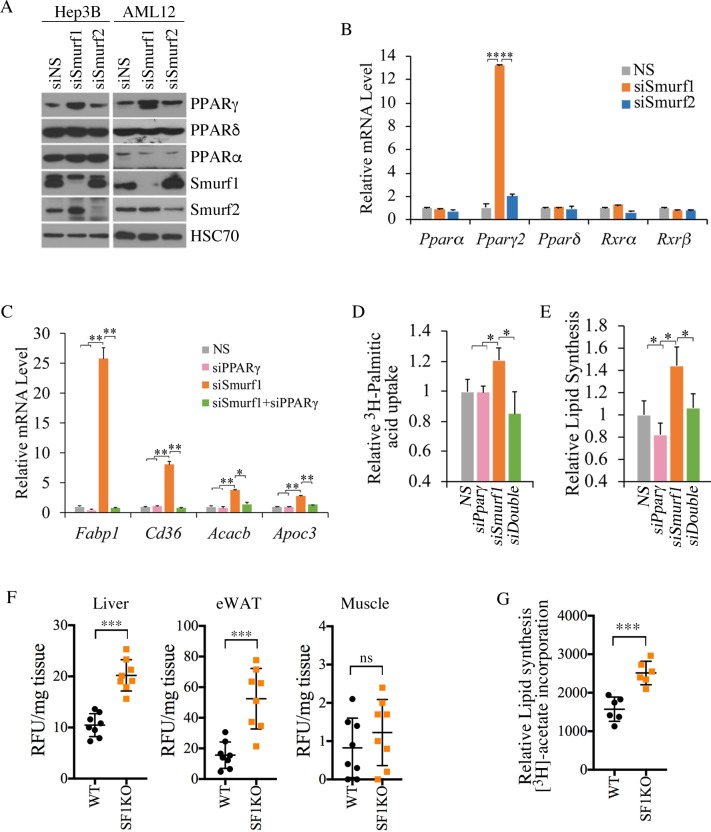
Fig 4. Smurf1 regulates fatty acid uptake and lipid synthesis through PPARγ.
(A) Western blots showing that knockdown of Smurf1 but not Smurf2 in Hep3B and AML12 cells increased PPARγ protein level. (B) qRT-PCR analyses showing that knockdown of Smurf1 but not Smurf2 increased Pparγ mRNA level in AML12 cells. (C) qRT-PCR analyses showing that knockdown of Smurf1 in AML12 cells increased expression of Fabp1, Cd36, Acacb, and Apoc3 in a PPARγ-dependent manner. (D) Fatty acid uptake in AML12 cells as measured by 3H-palmitate incorporation (n = 3). (E) Lipid synthesis in AML12 cells as measured by incorporation of 3H-acetate into lipid (n = 3). (F) In vivo fatty acid uptake after intraperitoneal injection of BODIPY-FL-C16. The BODIPY-FL-C16 accumulation in the liver, epididymal WAT, and skeletal muscle was normalized to tissue weight (n = 8 per group). (G) Lipogenesis in primary hepatocytes as measured by the incorporation of 3H-acetate into lipid (n = 6 per group). Data are presented as mean ± SD; statistical significance of difference is indicated as *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Original raw data can be found in S1 Data. BODIPY-FL-C16, 4,4-Difluoro-5,7-Dimethyl-4-Bora-3a,4a-Diaza-s-Indacene-3-Hexadecanoic Acid; eWAT, epididymal WAT; HSC70, heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein; NS, non-silencing control; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; qRT-PCR, quantitative real-time PCR; RFU, relative fluorescence units; Rxr, retinoid x receptor; SF1KO, Smurf1 KO; siNS, non-silencing control siRNA; Smurf, Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor; WAT, white adipose tissue; WT, wild-type.