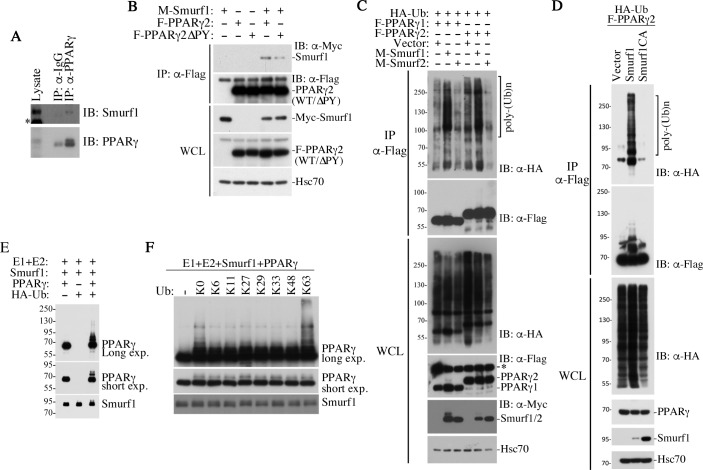
Fig 5. Smurf1 catalyzes non-proteolytic ubiquitination of PPARγ.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation showing interaction between endogenous Smurf1 and PPARγ in AML12 cells. *nonspecific band. (B) PY motif in PPARγ contributes to the interaction between Smurf1 and PPARγ. Myc-tagged Smurf1, Flag-tagged PPARγ2, and its ΔPY mutant were transfected into AML12 cells as indicated. WCL were immunoprecipitated with Flag-M2 beads and followed by western blot analyses. (C) Smurf1 but not Smurf2 promotes polyubiquitination of PPARγ1 and PPARγ2. Flag-PPARγ were immunoprecipitated from transfected AML12 and resolved by SDS-PAGE. Western blot analyses were carried out to detect HA-ubiquitin (top) and Flag-PPARγ1 or -γ2 (second panel) in the precipitates. The levels of total HA-Ub, Flag-PPARγ, Myc-Smurfs, and endogenous Hsc70 (loading control) in the WCL were also analyzed and are shown in the bottom panels. *nonspecific band. (D) E3 ligase activity of Smurf1 is required for Smurf1-mediated polyubiquitination of PPARγ. Flag-PPARγ2 and WT Myc-Smurf1 and its mutant Myc-Smurf1(CA) were transfected into the Smurf1KO MEFs along with HA-Ub. Ubiquitination of PPARγ2 was analyzed by western blot after Flag-M2 immunoprecipitation, as in C. (E) In vitro ubiquitination assay using recombinant proteins showing that PPARγ is a direct substrate of Smurf1-mediated polyubiquitination. (F) Smurf1 induces K63-linked polyubiquitination of PPARγ. Purified ubiquitin with no lysine residue (K0) or with single lysine residue at indicated position was used in the in vitro ubiquitination assay. E3, ubiquitin ligase; HA, human influenza hemagglutinin; Hsc70, heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein; IB, immunoblot; IP, immunoprecipitation; K, lysine; KO, knockout; MEF, mouse embryonic fibroblast; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; PY, PPxY; SDS-PAGE, sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; Smurf, Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor; Ub, ubiquitin; WCL, whole cell lysate; WT, wild-type.