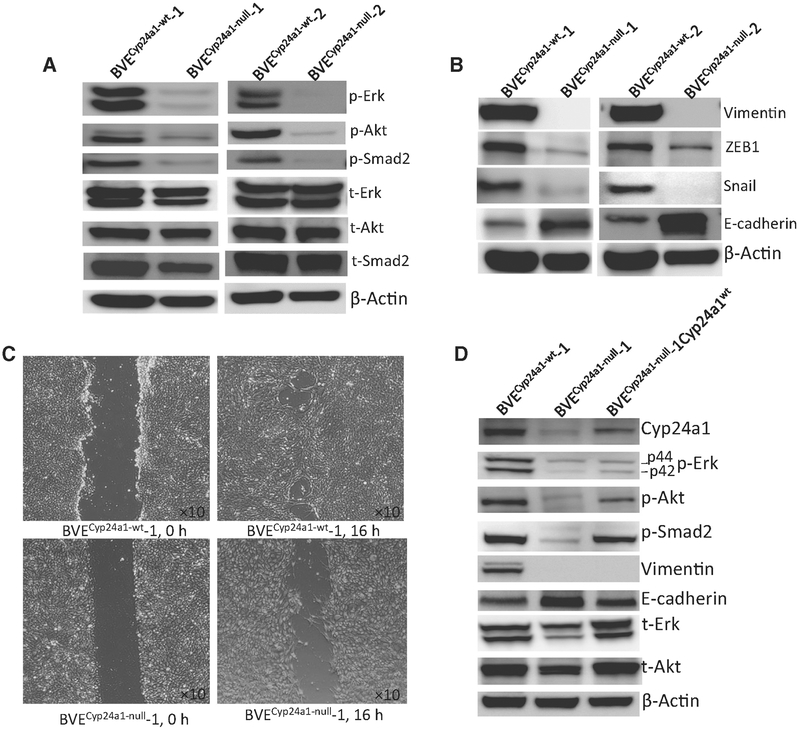
Figure 3.
Cyp24a1 knockout leads to downregulation of the MAPK, PI3K/Akt, TGF-β signaling pathways, and loss of EMT in the BVECyp24a1-null-derived tumor cells. A, Western blot analysis of the p-Erk, p-AKT, and p-Smad2 protein levels in BVECyp24a1-wt-1, BVECyp24a1-wt-2, BVECyp24a1-null-1, and BVECyp24a1-null-2 tumor cell lines. The phosphorylation of these proteins was decreased in both BVECyp24a1-null tumor cell lines. B, Western blot analysis of vimentin, ZEB1, Snail, and E-cadherin expression in BVECyp24a1-wt-1, BVECyp24a1-wt-2, BVECyp24a1-null-1, and BVECyp24a1-null-2 tumor cell lines. Snail and ZEB1 expression was reduced, whereas E-cadherin expression was increased in both BVECyp24a1-null cell lines. The expression of vimentin was not detected. C, Wound-healing assay. Cell migration was measured by the wound-healing assay. Cells were seeded in 6-well plates (105 cells/well) and a linear scratch was created when cells reached confluent monolayer. The cells were further cultured for 16 hours to observe wound healing or cell migration. The wound healing or cell migration is reduced in the BVECyp24a1-null cells. D, Western blot analysis of the CYP24A1, p-Erk, p-AKT, p-Smad2, vimentin, and E-cadherin protein levels in BVECyp24a1-null-1Cyp24a1 tumor cells. Increased phosphorylation of p-Erk, p-AKT, and p-Smad2 and decreased E-cadherin expression are shown in the BVECyp24a1-null-1Cyp24a1 tumor cells following reexpression of CYP24A1.