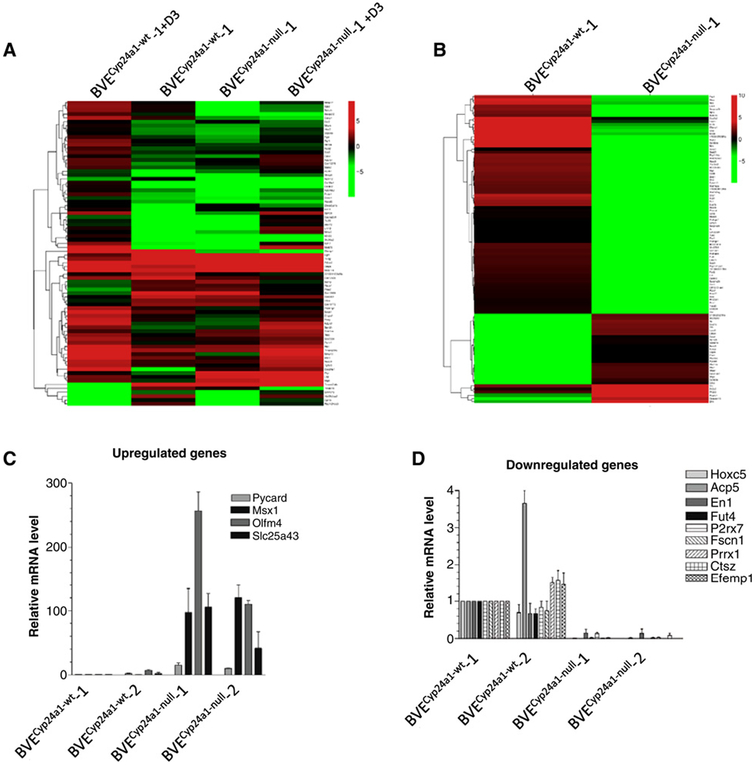
Figure 5.
RNA-Seq analysis of DEGs in the BVECyp24a1-null-derived tumor cells. A, Heat map of vitamin D–responsive genes in the BVECyp24a1-null-1-derived tumor cells. Both BVECyp24a1-wt-1 and BVECyp24a1-null-1 cell lines were treated with or without 100 nmol/L calcitriol for 16 hours. DEGs with log ratio of BVECyp24a1-wt −1 ± D3/BVECyp24a1-wt-1 > 2 were selected as vitamin D–responsive genes. A total of 80 DEGs was included and their expression levels were represented by a color range from green (low) to red (high). No significant changes were observed after Cyp24a1 deletion. B, Heat map of top 100 DEGs in the BVECyp24a1-null-1–derived tumor cells. The impact of Cyp24a1 deletion on the global gene expression was analyzed from 100 highly DEGs (log2-fold change >6.57). Significant changes in gene expression were demonstrated after Cyp24a1 deletion. C, qRT-PCR analysis of upregulated DEGs in the BVECyp24a1-null-1 and BVECyp24a1-null-2 cell lines. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of the relative mRNA level of target genes after normalization to β-actin expression. Results of BVECyp24a1-wt-1 were adjusted as 1. D, qRT-PCR analysis of downregulated DEGs in the BVECyp24a1-null-1 and BVECyp24a1-null-2 cell lines. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM of the relative mRNA level of target genes after normalization to b-actin expression. Results of BVECyp24a1-wt-1 were adjusted as 1.