Figure 6.
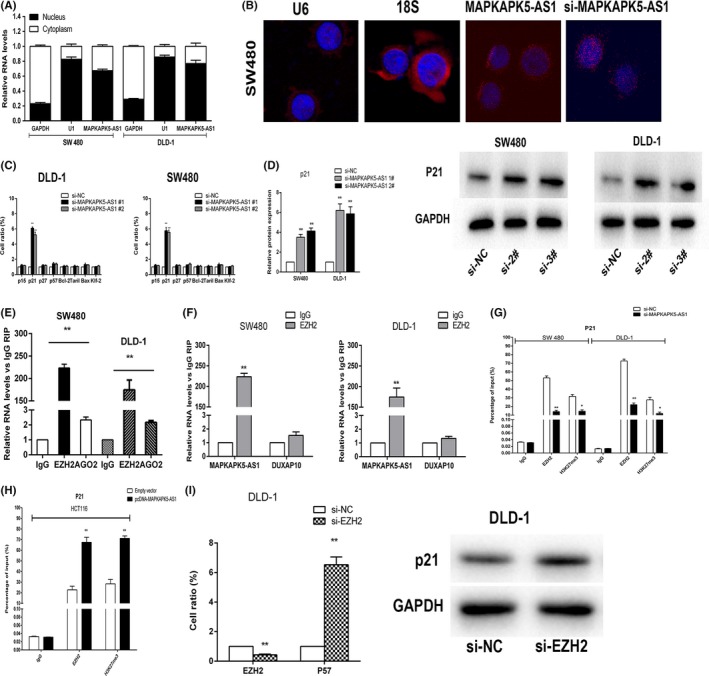
MAPKAPK5‐AS1 partly silences p21 transcription by binding to enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2). A, Expression levels of MAPKAPK5‐AS1 in cell nucleus and cytoplasm in DLD‐1 and SW480 cells investigated by quantitative RT‐PCR (qRT‐PCR). U6 was used as a nuclear marker, and GAPDH was used as a cytosol marker. B, FISH analysis of the location of MAPKAPK5‐AS1 (red) in the cytoplasm and nuclear fractions (blue) of SW480 cells. C, Eight classical mRNA expression levels D, Expression of p21 was determined after knockdown of MAPKAPK5‐AS1 by qRT‐PCR and western blot assays after transfection. E, RNA immunoprecipitation assays were carried out in DLD‐1 and SW480 cells, and the coprecipitated RNA was subjected to qRT‐PCR for MAPKAPK5‐AS1. F, DUXAP10 was used as negative control. G, ChIP‐qRT‐PCR of EZH2 occupancy and H3K27me3 binding in the p21 promoter in DLD‐1 and SW480 cells treated with si‐MAPKAPK5‐AS1 (48 hours) or the negative control (si‐NC); IgG as negative control. H, ChIP‐qRT‐PCR of EZH2 occupancy and H3K27me3 binding in the p21 promoter in HCT116 cells treated with pcDNA‐MAPKAPK5‐AS1; IgG as negative control. I, qRT‐PCR assays were used to determine the expression of EZH2 in DLD‐1 cells after EZH2 knockdown. p21 expression was investigated in DLD‐1 cells after knockdown of EZH2 through qRT‐PCR and western blot assays. Representative images and data based on 3 independent experiments. Bars: ± SD, *P < .05, **P < .01
