Figure 4. TET2 Is Recruited by SNIP1 to Regulate c-MYC Target Gene Expression.
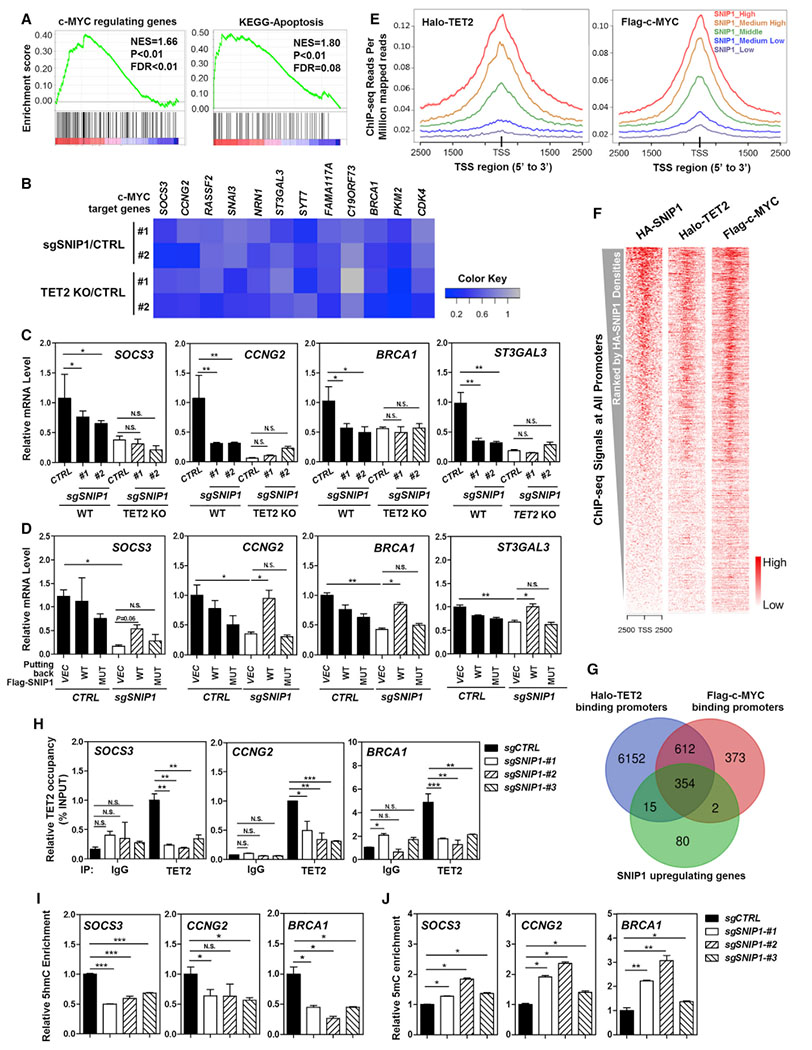
(A) RNA sequencing analysis reveals that SNIP1 knockdown causes significant alterations in mRNA expression of genes that are c-MYC targets or involved in cell apoptosis. More detailed information is provided in STAR Methods.
(B) Real-time qPCR confirms that c-MYC target genes are commonly downregulated by SNIP1 knockdown or TET2 knockout in U2OS cells. Data were normalized by mRNA expression in control cells. A gray-to-blue color scale indicates values from no change to downregulation, and row scaling is used to facilitate visualization.
(C) SNIP1 knockdown and TET2 knockout do not have an additive effect on downregulating c-MYC target genes. In SNIP1-knockdown and/or TET2-knockout U2OS cells, mRNA expression of the indicated c-MYC direct target genes was determined using real-time qRT-PCR, as described in STAR Methods.
(D) TET2 association is indispensable for SNIP1 to activate c-MYC target genes. Wild-type or TET2-binding defective K30A/P100A/K108A mutant SNIP1 was overexpressed in SNIP1-knockdown U2OS cells, and mRNA expression of the indicated c-MYC direct target genes was determined using real-time qRT-PCR.
(E–G) Enrichment of ectopically expressed TET2, SNIP1, and c-MYC in the genome of HEK293T cells. Previous ChIP-seq data (GSM897576 and GSM1493021) were re-analyzed using Bowtie 1.2.1.1 (Langmead et al., 2009) and MACS 2.1.1 (Zhang et al., 2008). ChIP-seq densities of Halo-TET2 and Flag-c-MYC were profiled according to the indicated levels of HA-SNIP1 ChIP-seq signals around TSS regions (E). Heatmap analysis of total 27,569 TSSs showed that HA-SNIP1, Halo-TET2, and Flag-c-MYC had similar binding patterns across all TSSs. All TSSs were ranked by HA-SNIP1 signal intensities (F). The overlap of TET2 and c-MYC-binding promoters and SNIP1 upregulating genes in U2OS identified by RNA-seq is displayed by Venn diagram (G) (p < 10−10).
(H) TET2 binds to c-MYC target gene promoters in a manner dependent on SNIP1. In SNIP1-knockdown and the control U2OS cells, the occupancy of endogenous TET2 on the promoters of indicated c-MYC target genes was determined using ChIP-qPCR as described in STAR Methods. Rabbit IgG was used as a negative control.
(I and J) SNIP1 knockdown decreases 5hmC and increases 5mC at the promoters of c-MYC target genes. In SNIP1-knockdown and the control U2OS cells, 5hmC and 5mC levels at the promoter regions of indicated c-MYC direct target genes were determined using hMeDIP-qPCR (I) and MeDIP-qPCR (J), respectively, as described in STAR Methods.
Shown are average values of triplicated experiments with SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 for the indicated comparisons. N.S., not significant.
