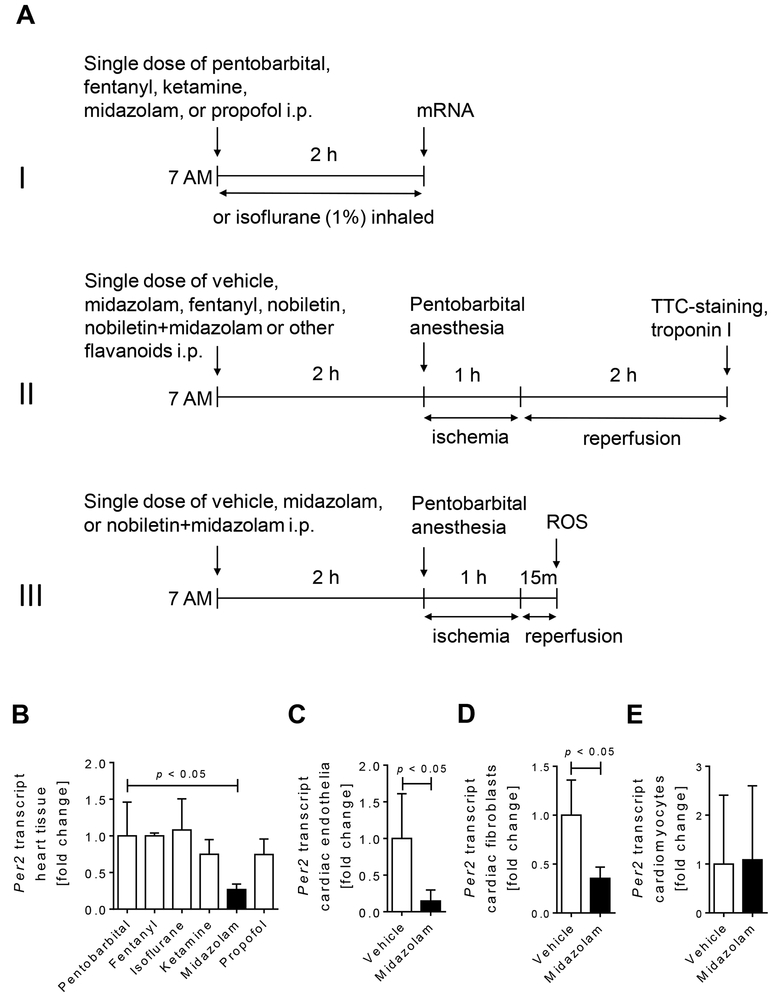
Figure 1. Studies of cardiac Per2 regulation following exposure of wildtype mice to anesthetics.
Wildtype mice were exposed to a single dose of pentobarbital (70 mg/kg i.p.), fentanyl (1 mg/kg i.p.), isoflurane (1% inhaled), ketamine (200mg/kg i.p.), propofol (200 mg/kg i.p.), or midazolam (200 mg/kg i.p.). Two hours later cardiac Per2 mRNA expression levels were analyzed. In a subset of experiments murine endothelia, fibroblasts or cardiomyocytes were exposed to vehicle (NaCl 0.9%) or midazolam for 6 hours. Total RNA was isolated by Qiazol Reagent (Qiagen) and chloroform extraction in conjunction with the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen), following the manufacturer’s instructions (SA-Biosciences, Qiagen). cDNA from mRNA was generated using iScript (Bio-Rad) and transcript levels were determined by real-time RT-PCR (iCycler; Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.). (A) Overview and timeline of all in vivo studies. (I) Screening of different anesthetics for their effect on mouse heart Per2 mRNA levels. (II) Myocardial ischemia and reperfusion studies. (III) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) measurements following myocardial ischemia. (B) Mouse cardiac Per2 mRNA levels two hours after exposure to different anesthetics. (C) Per2 mRNA levels from murine cardiac endothelia after 6 h of midazolam (50μM) exposure. (D) Per2 mRNA levels from murine cardiac fibroblasts after 6 h of midazolam (50μM) exposure. (E) Per2 mRNA levels from isolated murine cardiomyocytes after 6 h of midazolam (50μM) exposure; (mean±SD, n=4–6; p<0.05).