Figure 3. Mutated HRAS and BRAF can transform non-PcSC WAP+ cells in the hyperplastic lesion of MMTV-Wnt1 mammary glands.
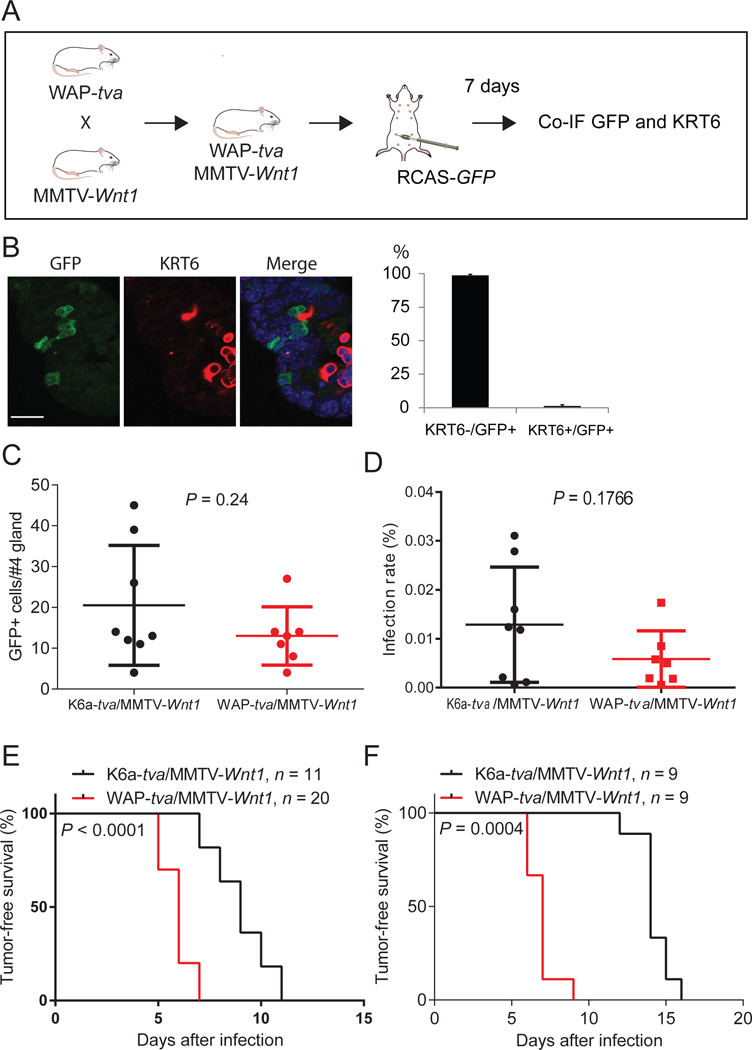
(A) Diagram of experimental design to examine whether TVA+ cells from WAP-tva/MMTV-Wnt1 contain Krt6+ cells. Co-IF, co-immunofluorescent staining. (B) Co-IF of GFP and KRT6 on mammary glands generated from experiment shown in A. The quantification of the percentages of KRT6- and KRT6A+ cells among GFP+ cells are shown next to the image. n = 3, mouse age = 13 weeks. Scale bar = 20μm. (C and D) Identification of the dosages of RCAS virus used to infect similar small numbers of cells in Krt6a-tva/MMTV-Wnt1 vs. WAP-tva/MMTV-Wnt1 mammary glands. The doses of 4×106 and 1×105 IUs of RVAS-GFP per gland for Krt6a-tva/MMTV-Wnt1 and WAP-tva/MMTV-Wnt1 mice, respectively, infected similar small numbers of cells (C) and percentages of cells (D). (E and F) Tumors can be induced from both KRT6A+ and WAP+ cells in MMTV-Wnt1 mammary precancerous lesions by HRASQ61L or BRAFV600E. Kaplan-Meier tumor-free survival plots of K6a-tva/MMTV-Wnt1 and WAP-tva/MMTV-Wnt1 mice infected by RCAS-HrasQ61L (D) and RCAS-BRAFV600E (E), respectively. The virus dosages used were the same as used in C and D.
