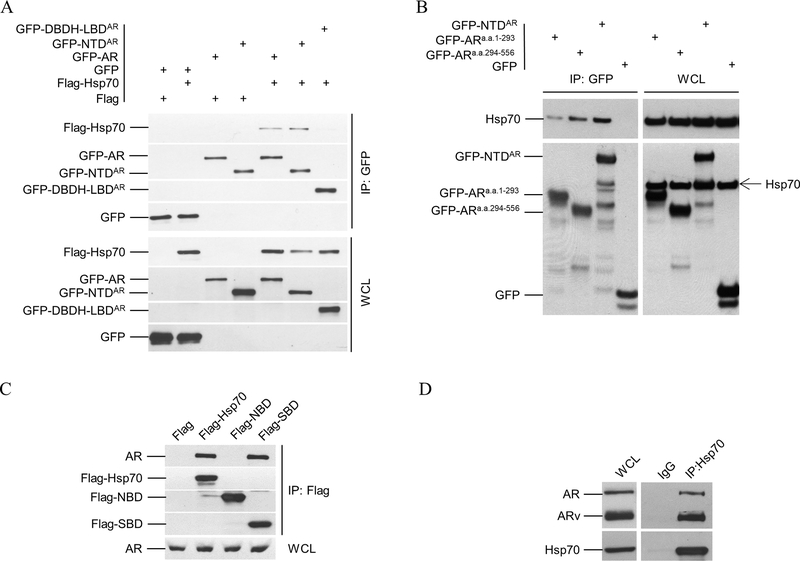
Figure 3.
Co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) analysis of Hsp70 and AR interaction. A. Flag-tagged Hsp70 was co-transfected with GFP-tagged AR or its deletion mutants into PC3 cells. Whole cell lysates (WCL) were prepared for co-IP using anti-GFP beads. Both WCL and immnoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Flag antibody and then anti-GFP antibody. B. C4–2 cells were transfected with expression vectors for GFP-tagged NTD, AR(1–293), and AR(294–556), along with GFP control. Co-IP were performed similarly as in A. The WCL and immnoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Hsp 70 antibody and then anti-GFP antibody. C. Expression vectors for GFP-tagged Nucleotide Binding domain (NBD a.a. 1–386) and Substrate Binding Domain (SBD a.a. 386–641) of Hsp70 were transfected into C4–2 cells separately. Co-IP and immunoblotting were performed similarly as in A using anti-Flag and anti-AR antibodies. D. 22Rv1 cell lysates were prepare for co-IP using anti-Hsp70 antibody or IgG. 22Rv1 cells express full-length AR and its splice variants, including AR-V7 that lacks LBD. The WCL and immnoprecipitates were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-AR antibody and then anti-Hsp70 antibody. All experiments were reproduced at least twice.