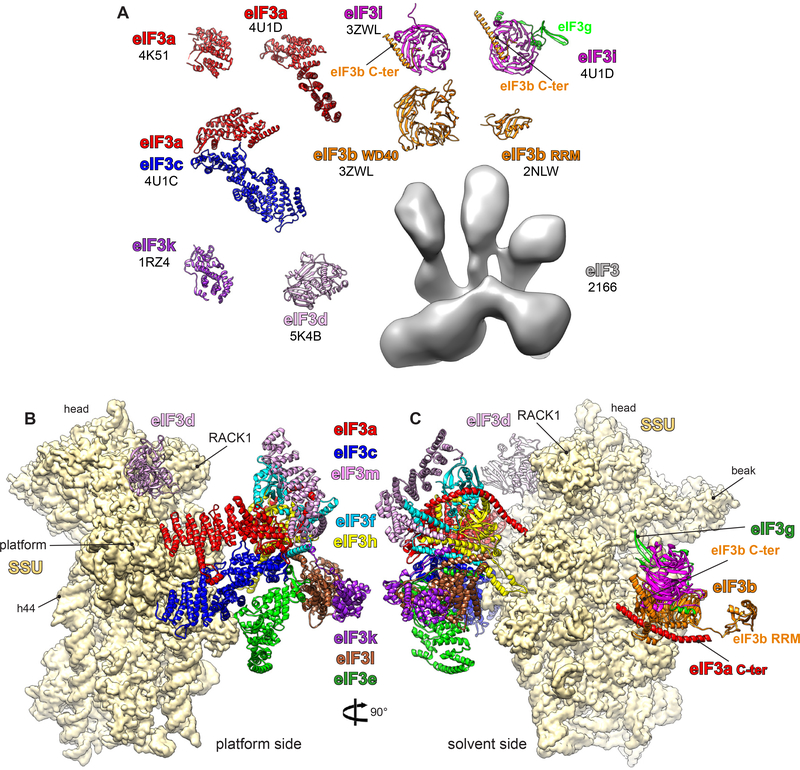
Figure 2.
Structures of eIF3 fragments and subunits by X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance, and cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM). (a) Different fragments of eIF3 subunits are colored variably, and the accession codes are written in black below the name of each subunit. (b,c) Small subunit (SSU) shown in yellow surface, and eIF3 in colored ribbons. Different eIF3 subunits are labeled and colored variably. The displayed eIF3 structure is a model derived from an ~6-Å cryo-EM map of the mammalian 43S preinitiation complex (30), which was in part interpreted thanks to the high-resolution structures of eIF3 fragments. Additional abbreviations: C-ter, C-terminus; eIF, eukaryotic initiation factor; h44, helix 44; RRM, RNA recognition motif.