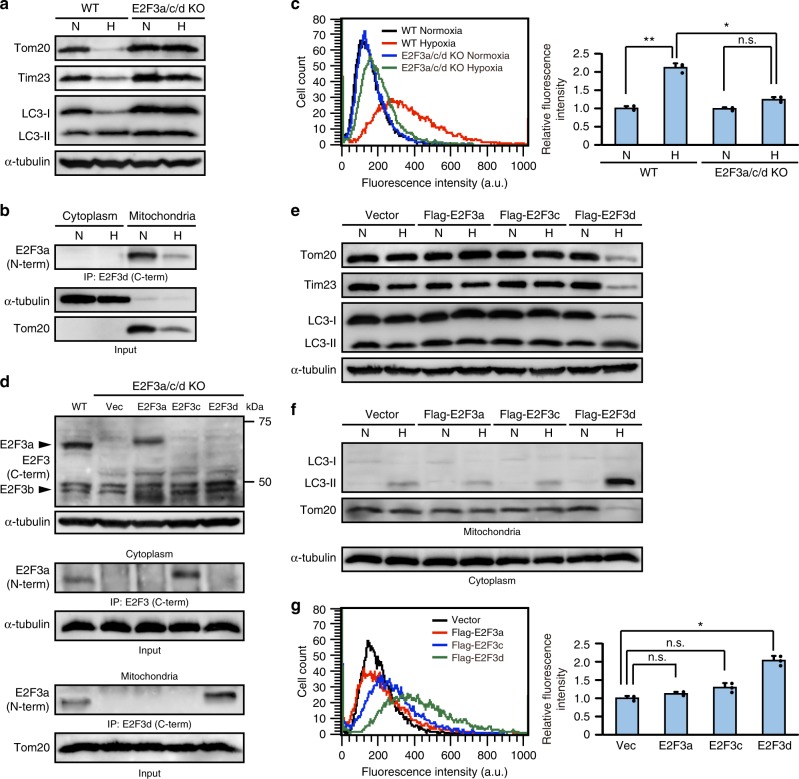
Fig. 4.
E2F3d is important for hypoxia-induced mitophagy. a–c Parental WT and E2F3a/c/d KO HeLa cells were cultured under normoxic (N; 21% O2) or hypoxic (H; 1% O2) conditions for 24 h. a Cell lysates were examined by immunoblotting. b Cytoplasmic and mitochondrial lysates from parental WT cells were immunoprecipitated with the antibody against the C-terminal domain of human E2F3d protein and probed with the antibody against the N-terminal domain of human E2F3a protein. c The uptake of mitochondria by lysosomes was evaluated by mitophagy assay. Data are presented as the mean of three independent experiments (≥10,000 cells). Error bars represent SD. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. n.s. not significant, a.u. arbitrary units. d–g E2F3a/c/d KO HeLa cells were infected with control retrovirus (Vec) or retroviruses expressing Flag-E2F3a, Flag-E2F3c, or Flag-E2F3d. d Cell lysates were examined by immunoblotting (top). Cytoplasmic (middle) and mitochondrial (bottom) lysates were immunoprecipitated with the antibodies against the C-terminal domains of human E2F3a or E2F3d proteins, and probed with the antibody against the N-terminal domain of human E2F3a protein. e, f Cells were cultured under normoxic or hypoxic conditions for 24 h. Cell lysates (e) and cytoplasmic lysates and mitochondria (f) were examined by immunoblotting. g Cells were cultured under hypoxic conditions for 24 h and the uptake of mitochondria by lysosomes was analyzed as described in c. *P < 0.05. n.s. not significant. Full-size scans of immunoblots are shown in Supplementary Information. Please see Supplementary Fig. 5