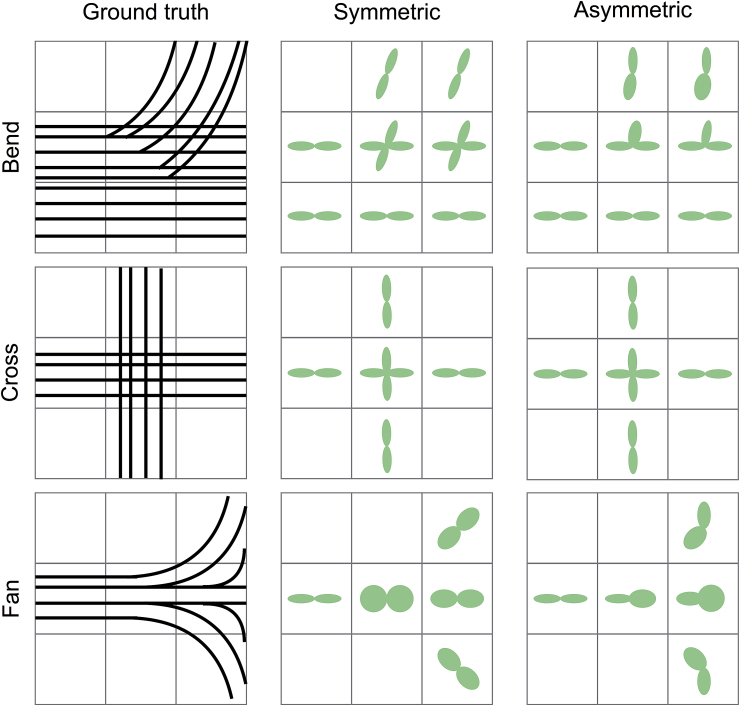
Fig. 1.
Toy examples of 3 different complex fibre patterns: sharp bend (top row), fibre crossing (middle row) and fibre fanning (bottom row). When using symmetric fods (middle column), sharp bending and fanning patterns cannot be accurately represented. When using asymmetric fods (rightmost column), only the meaningful fod peaks are selected both in the sharp bending and fibre crossing cases. Moreover, the right fanning polarity (i.e., increased dispersion along the left-right orientation) can be obtained.