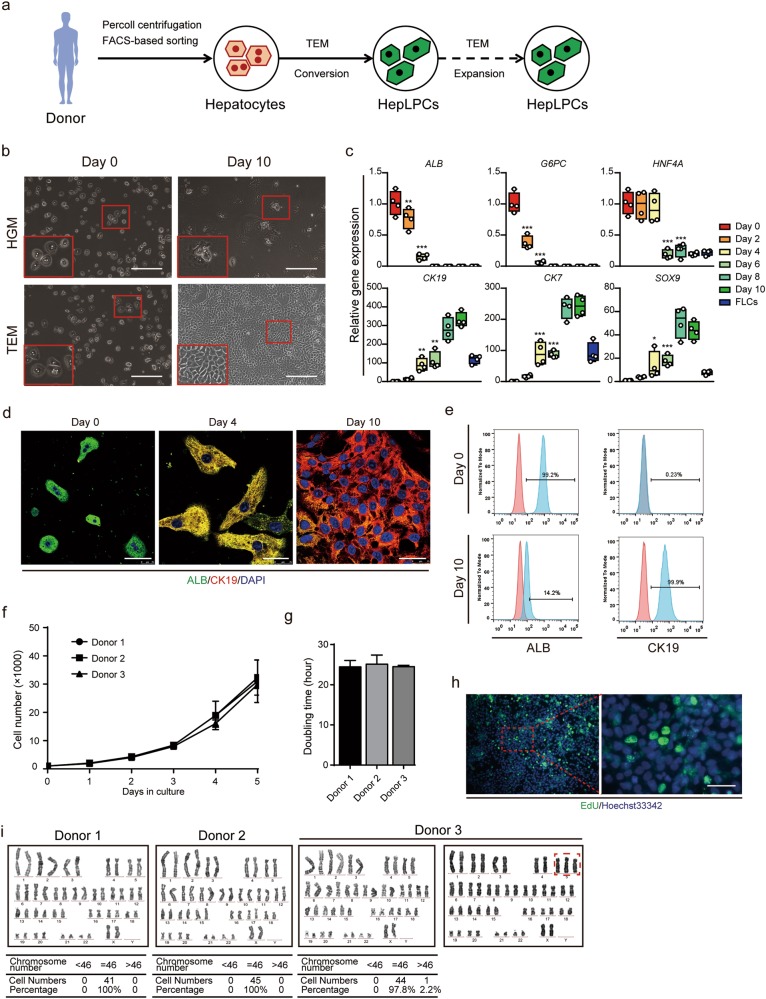
Fig. 1.
Generation of human hepatocytes-derived liver progenitor-like cells in vitro. a Overview of the protocol used to convert PHCs into HepLPCs. b Light microscopy images of PHCs cultured in HGM or TEM at day 0 and day 10. Scale bars, 200 µm. c QPCR analyses for the expression of the indicated genes during TEM culture from day 0 to day 10. FLCs, fetal liver cells, 5 gestational weeks (one-way ANOVA with Dunnett correction for multiple comparisons, n = 4 donors, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). d Immunofluorescence analyses demonstrating the expression of ALB and CK19. Scale bars, 50 µm. e Flow cytometric analysis showing the proportion of ALB or CK19 positive-cells in the populations. Blue, positive-cells; red, negative controls. f Growth curves illustrate the number of cells counted per well at different time points. Results expressed as mean ± s.d. of three independent cultures derived from three donors. g Doubling time calculated for three donors. Error bars represent s.d.; n = 3. h Edu incorporation is detected at passage 10. Scale bar, 50 µm. i Representative karyotype images of three independently established HepLPCs. Two lines maintained normal diploid karyotypes, whereas the third was partly triploid for Chromosome 5