Fig. 3.
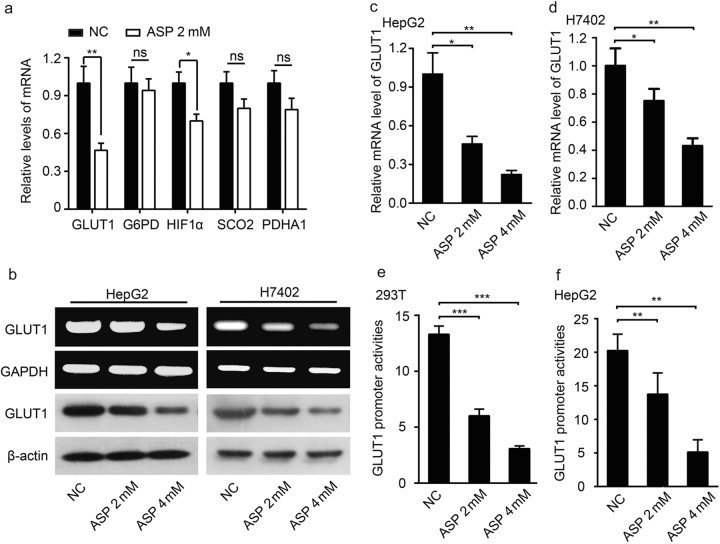
Aspirin downregulates the GLUT1 expression through suppressing its transcriptional activities in hepatoma cells. a The cells were treated with indicated concentrations (2 mM) of aspirin for 48 h. The mRNA of GLUT1, G6PD, HIF1α, SCO2, and PDHA1 were examined by RT-qPCR. b The expression levels of GLUT1 were separately detected by RT-PCR and Western blot assay, in HepG2 (left) and H7402 cells (right). The cells were treated with indicated concentrations of aspirin for 48 h. c The expression levels of GLUT1 in HepG2 cells were separately detected by RT-qPCR assay. d The expression levels of GLUT1 in H7402 cells were separately detected by RT-qPCR assay. e Luciferase reporter gene assay was detected in 293T cells transiently transfected with pGL3-P1 (0.2 μg/well) and treated with indicated concentrations of aspirin (0, 2, 4 mM) for 48 h. f Luciferase reporter gene assay were measured in HepG2 cells transiently transfected with pGL3-P1 (0.2 μg/well) and treated with indicated concentrations of aspirin for 48 h. Statistical significant differences are indicated: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, Student’s t-test for (a), one-way ANOVA for (c–f). All experiments were performed at least three times