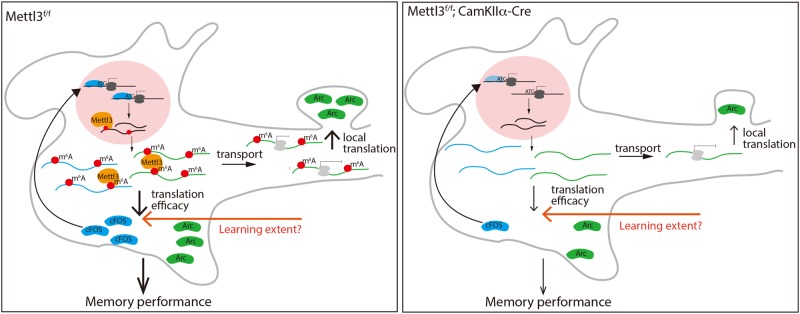
Fig. 1.
Regulation of memory strength by METTL3. Left panel: METTL3-mediated m6A modification might influence translation efficacy, mRNA transport and local translation of IEGs by m6A readers and writers to modulate learning-induced plasticity in neurons. Right panel: Lack of m6A modification in METTL3-deficient animals prevents additional mRNA processing and leads to decreased levels of IEGs, and decreased memory performance. The decrease in IEG translation might be overcome by m6A modification-independent mechanisms induced through increased learning