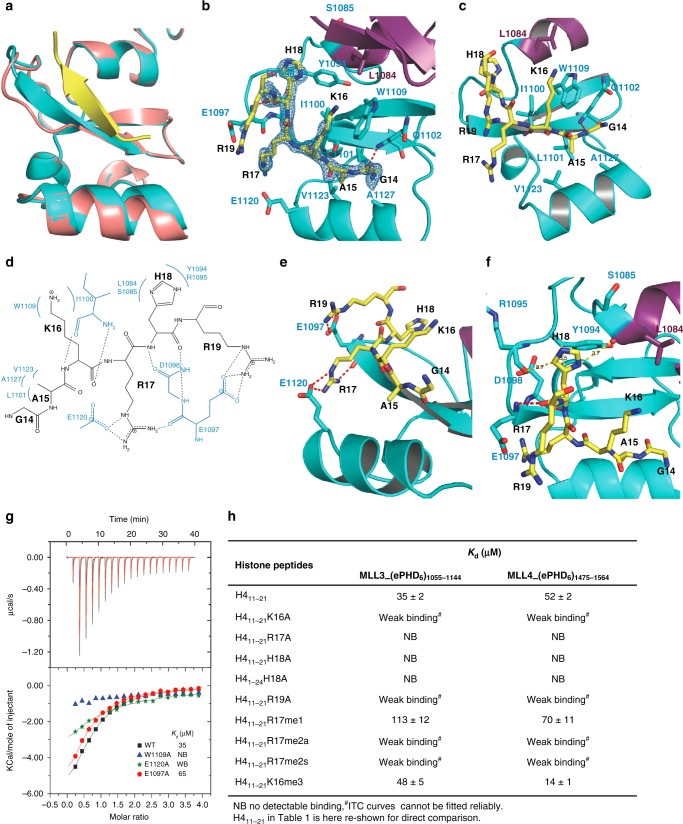
Fig. 2.
The ePHD6 domain of MLL3 specifically binds to the H4H18-containing motif of histone H4. a Superimposition of the structures of the H4 peptide-bound and peptide-free ePHD6 domain of MLL3. b Cartoon representation of the PHD6 and preceding zinc finger colored in cyan and purple, respectively. The histone H4 peptide is shown with a Fo–Fc omit map contoured at 2.5 σ. c, e, f Detailed interactions between the ePHD6 domain of MLL3 and residues A15/K16, R17/R19, and H18 of histone H4 peptide, respectively. The histone H4 peptide is shown in sticks and colored in yellow. Interacting residues are shown in stick mode and red/yellow dashed lines represent intra-molecular hydrogen bonds and atom distances, respectively. d Schematic of the detailed interactions between the ePHD6 domain of MLL3 and the H4H18 histone H4 peptide. The histone H4 interacting residues of MLL3 are colored in blue. Dashed lines represent hydrogen bonds. g ITC curves for the titration of wild type or different mutants of ePHD6 domain of MLL3 to the histone H4 peptide H411–21. NB no detectable binding, WB, weak binding. h Binding affinities of different histone peptides to ePHD6 domain of MLL3 and MLL4 measured by ITC