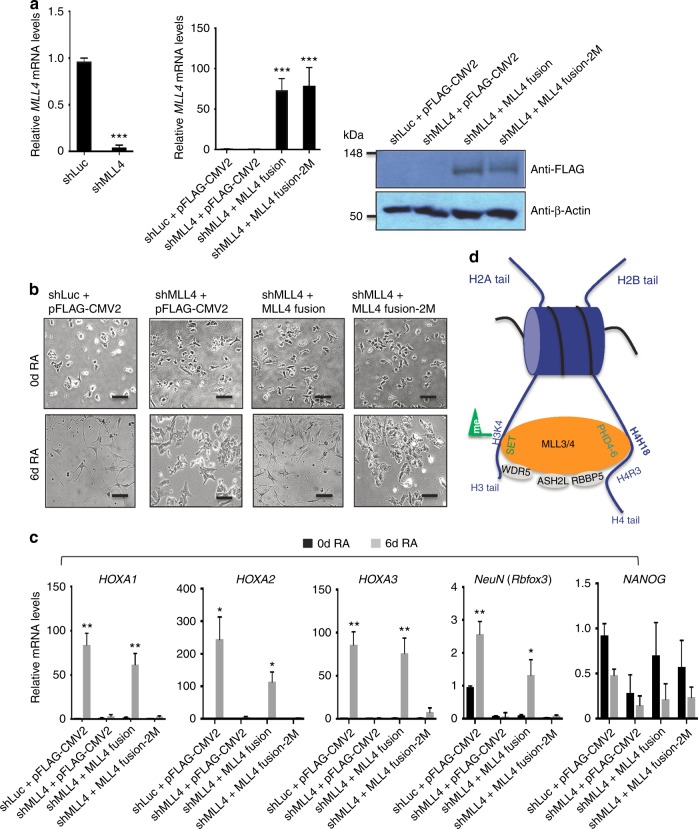
Fig. 4.
The binding activity of ePHD6 is essential for MLL4-mediated gene activation and cell-morphological changes during RA-induced NT2/D1 cell differentiation. a The efficiency of knockdown of MLL4 by shMLL4 (left) and rescue by ectopic expression of MLL4 fusion or MLL4 fusion-2M (W1529A/E1540A) (right) were examined by quantitative RT-PCR or western blot analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (error bars) of three independent experiments. Where indicated, statistical P-values were determined using two-tailed Student’s t-test. ***p < 0.001 indicate statistically significant differences. b The effect of ectopic expression of MLL4 fusion or MLL4 fusion-2M (W1529A/E1540A) on differentiation morphologies during RA-induced neuronal differentiation of shMLL4-treated NT2/D1 cells. Morphological changes during cellular differentiation were monitored using a microscope (10×). Shown are representative images of three independent experiments. Black scale bars, 50 µm. c The effect of MLL4 fusion or MLL4 fusion-2M on expression of the HOXA1‒3, NeuN, and NANOG genes during RA-induced neuronal differentiation of shMLL4-treated NT2/D1 cells. Expression levels were measured by quantitative RT-PCR. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (error bars) of three independent experiments. Where indicated, statistical P-values were determined using two-tailed Student’s t-test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 indicate statistically significant differences. d A possible model of the interaction between MLL3/4 and nucleosome. MLL3/4 are recruited to their targeted sites by the interaction between the PHD4-6 (ePHD6) domains and histone H4, and then the SET domains of MLL3/4 catalyze the methylation of histone H3K4 of the same or the nearby nucleosome