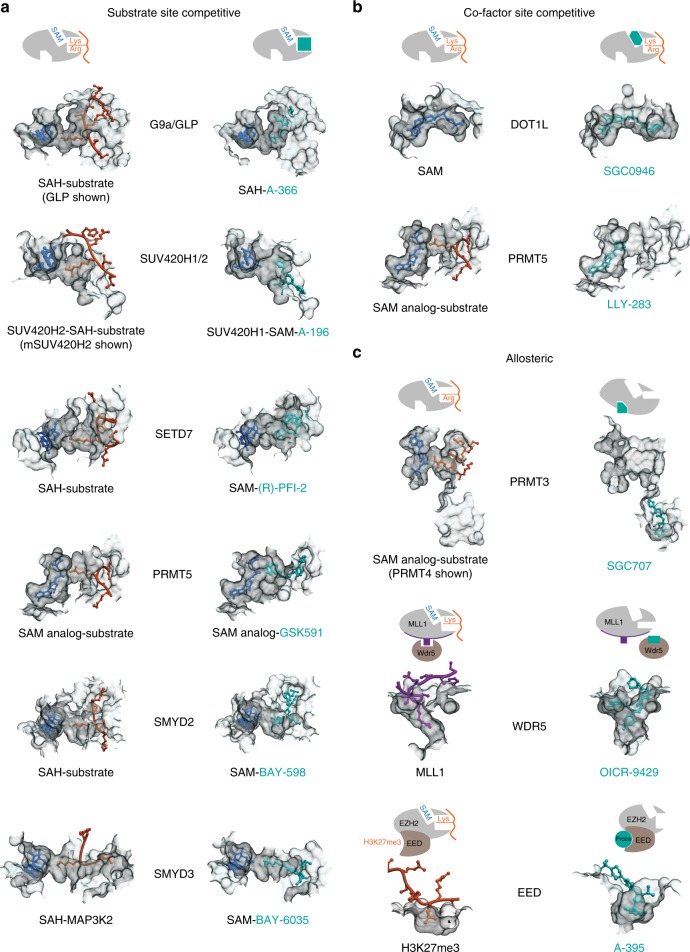
Fig. 2.
Structural mechanisms of PMT inhibition by chemical probes. a Inhibitors of G9a (PDB: 3HNA (GLP with H3K9 substrate) and 4NVQ (A-366)); SUV420H2 (PDB: 4AU7 (mSUV420H2 with H4 substrate) and SUV420H1 (PDB: 5CPR (A-196)); SETD7 (PDB: 1O9S (H3 substrate) and 4JLG (PFI-2)); PRMT5 (PDB: 4GQB (H4 substrate) and 5C9Z (GSK591)); SMYD2 (PDB: 3TG5 (p53 substrate) and 5ARG (BAY-598)); SMYD3 (PDB: 5EX0 (MAP3K2 substrate) and (BAY-6035)) all bind in the substrate (peptide) binding pocket. b SGC0946 binds in the SAM-binding pocket of DOT1L thereby preventing cofactor binding (PDB ID: 3QOW (SAM), 4ER6 (SGC0946)). LLY-283 also occupies the SAM-binding pocket of PRMT5-MEP50 complex (PDB ID: 4GQB (SAM analog) and 6CKC (LLY-283)). c Three distinct modes of allosteric inhibition of protein methyltransferases. SGC707 binds to PRMT3 in an allosteric site that prevents productive formation of the enzyme’s activation helix (PDB ID: 4RYL). OICR-9429 binds to WDR5 and inhibits MLL1 activity by disrupting WDR5-MLL1-RBBP5 complex (PDB ID: 4QL1). A-395 binds to the EED subunit of the PRC2 complex thereby preventing binding of activating peptides (PDB ID: 5K0M)