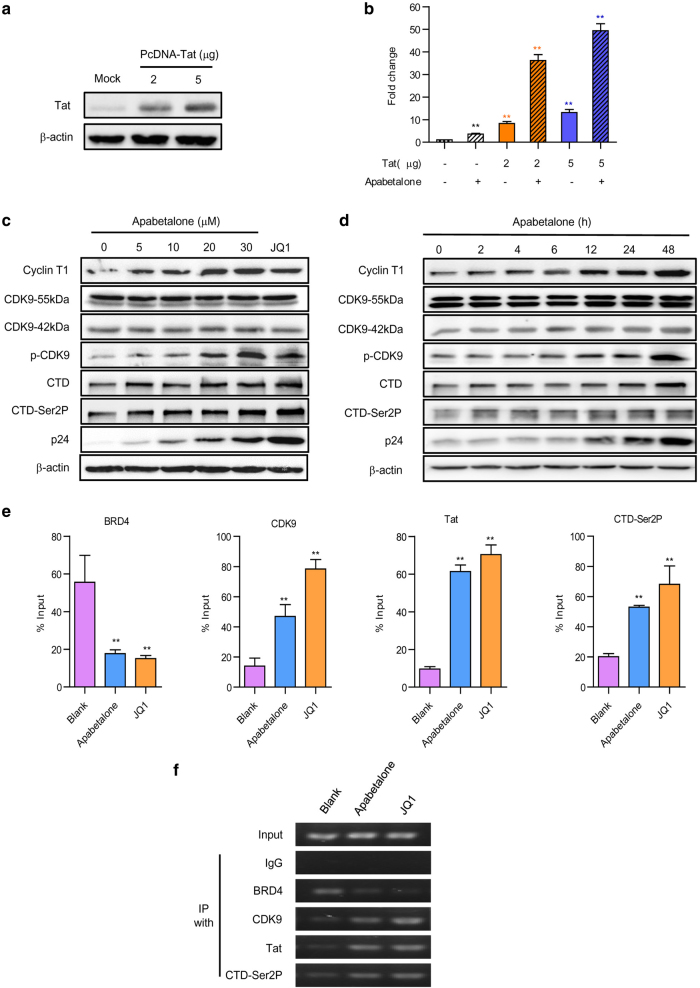
Fig. 4.
Apabetalone stimulated latent HIV-1 via a Tat-dependent P-TEFb pathway. a The model of TZMbl cells transfected with Tat. HeLa-based TZMb1 cells were nucleofected with a plasmid expressing Tat ( + ) or a negative control plasmid ( − ) for 48 h; after which detected with Tat antibodies by western blotting. b Apabetalone predominantly stimulated Tat-dependent HIV-1 transcription. Whole cell extracts were assayed for luciferase activity. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01. Apabetalone increased cyclin T1 expression and induced CDK9 T-loop and RNAP II CTD phosphorylation in ACH2 cells in c dose-dependent and d time-dependent manners. e Apabetalone-induced BRD4 dissociation enabled Tat to recruit P-TEFb to the HIV promoter. The signals were normalized to those of the input. The error bars in all panels represent the mean ± SD. f The images were from agarose gel electrophorese. The input was made as 10% total amount and IgG was made as negative control