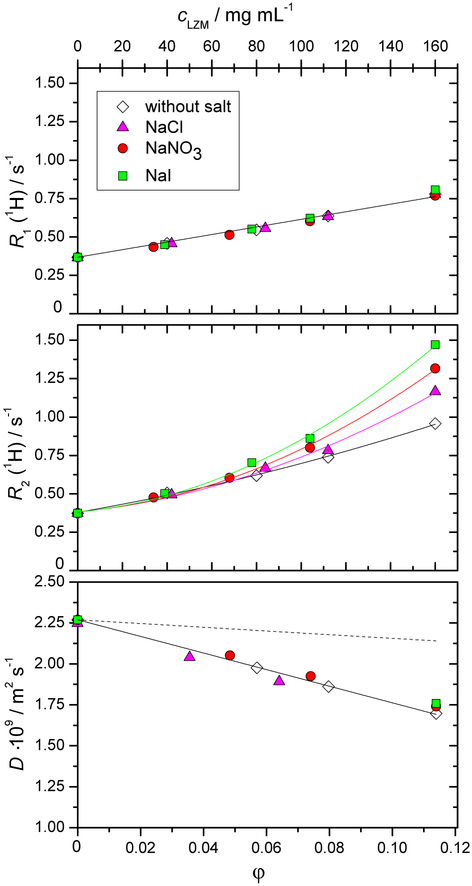
Fig. 1.
Dependence of the longitudinal relaxation rate R1 (panel a), trans-verse relaxation rate R2 (panel b), and the self-diffusion coefficient D (panel c) of the water proton as a function of the lysozyme mass concentration, cLZM. All solutions were prepared in the acetate buffer with pH = 4.6. The molar concentration of the low molecular mass salt (NaCl, NaNO3, or NaI) added to the aqueous protein-buffer solution was 0.1 mol L−1. All experiments were performed at T = 25 °C. The dashed line in panel c corresponds to a purely geometrical obstruction model, which links the diffusion coefficient, D, to the volume fraction occupied by the solutes, ϕ, according to D = D0(1 − φ/2) (D0 is the value for pure water). Experimental error bars are smaller than the symbol size for panels a and b, and approximately 2 % of the values in panel c. The volume fraction φ was computed using the molar volume of LZM of 0.712 mL g−1 according to Ref.69.