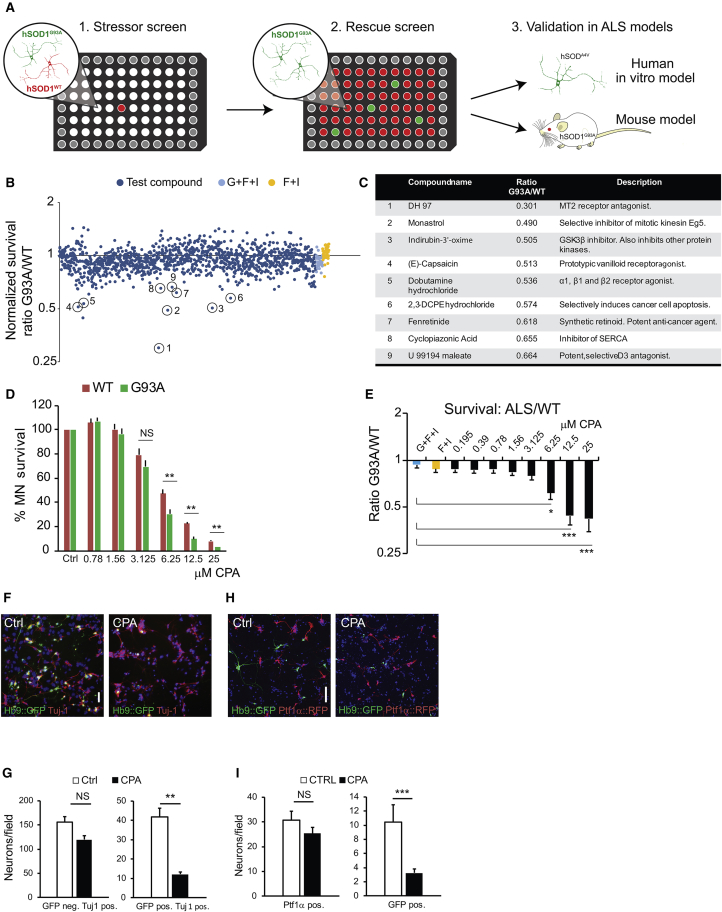
Figure 1.
Results from a Dual-Color Motor Neuron Stressor Screen: Dose-Respone Characterization of a Lead Compound and Subtype-Dependent Neuronal Survival
(A) Overview of the experimental design from primary stressor screen to secondary rescue screen and subsequent validation models. (B) Results of small molecule screen at 48 hr of exposure. Dark blue data points denote normalized G93A:WT survival ratio for well exposed to compounds, and light blue (negative control, GDNF + forskolin + IBMX + vehicle) and yellow data points (positive control, forskolin + IBMX + vehicle) denote G93A:WT survival ratio for the controls. (C) Circles mark confirmed lead compounds after secondary screening. (D and E) Dose-response curve (D) for cyclopiazonic acid (CPA), showing survival of Hb9::RFP hSOD1WT and Hb9::GFP hSOD1G93A motor neurons and normalized G93A:WT survival ratio (E). Results were compiled using two independent pairs of WT-G93A cell lines; individual results are shown in Figures S2A and S2B. Bars denote average, and error bars indicate SEM; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 (n = 9, one-way ANOVA, post hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparison). (F and G) Light microscope micrographs (F) showing control and CPA-treated motor neuron cultures. Scale bar, 50 μm. Survival of ctrl and CPA-exposed hSOD1G93A GFP+ motor neurons and Tuj-1+ GFP− neurons was quantified (G) at 48 hr (n = 3). (H and I) Light microscope micrographs (H) showing control and CPA-treated non-purified motor neuron-interneuron co-cultures. Survival of GFP+ hSOD1WT motor neurons and Ptf1α+ interneurons was quantified (I) at 48 hr (n = 3). Scale bar, 50 μm. Survival of GFP+ hSOD1WT motor neurons and Ptf1α+ interneurons was quantified at 48 hr (n = 3 for both analyses). Bars denote average, and error bars indicate SEM; **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001 (n = 3, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test).