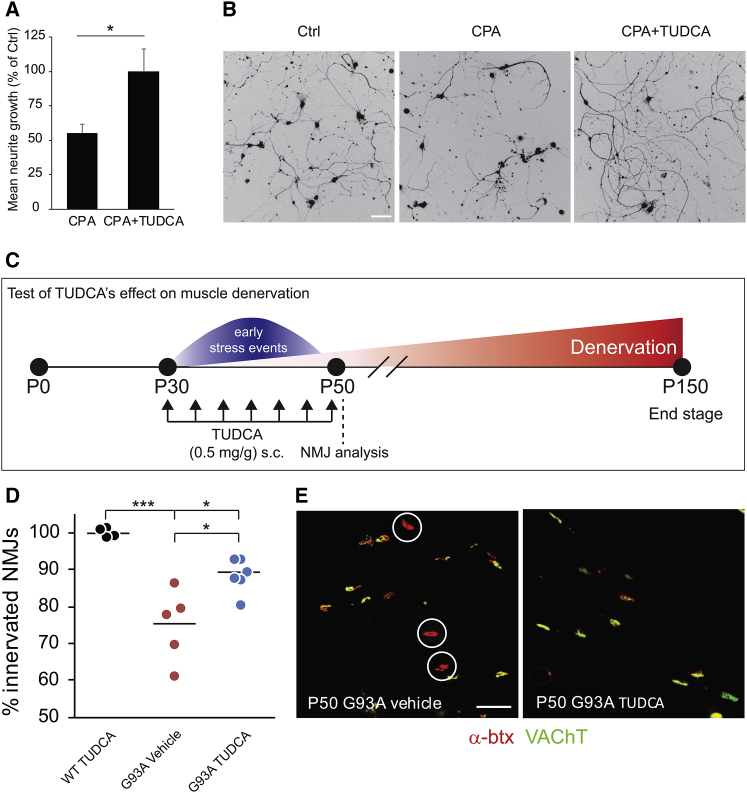
Figure 4.
Characterization of TUDCA’s Effects In Vitro and on Muscle Denervation In Vivo in a Mouse Model of ALS
(A) Histogram showing rescue effects of TUDCA on CPA-induced neurite degeneration. Bars denote average, and error bars indicate SEM; *p < 0.05 (unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test). (B) Representative light microscope micrographs showing the effects of TUDCA application in cultures exposed to CPA. Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Experimental design for the in vivo test of TUDCA on muscle denervation in hSOD1G93A mice. (D) Scatterplot showing NMJ innervation in the TA (n = 4 for WT + TUDCA, n = 6 for G93A + TUDCA, and n = 5 for G93A + vehicle). Data points represent individual animals, and horizontal lines denote the average; *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001 (one-way ANOVA, post hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparison test). (E) Confocal micrographs showing images from TA NMJs (α-btx, red; VAChT, green) of vehicle and TUDCA-treated hSOD1G93A mice. Circles denote denervated NMJs. Scale bar, 50 μm.