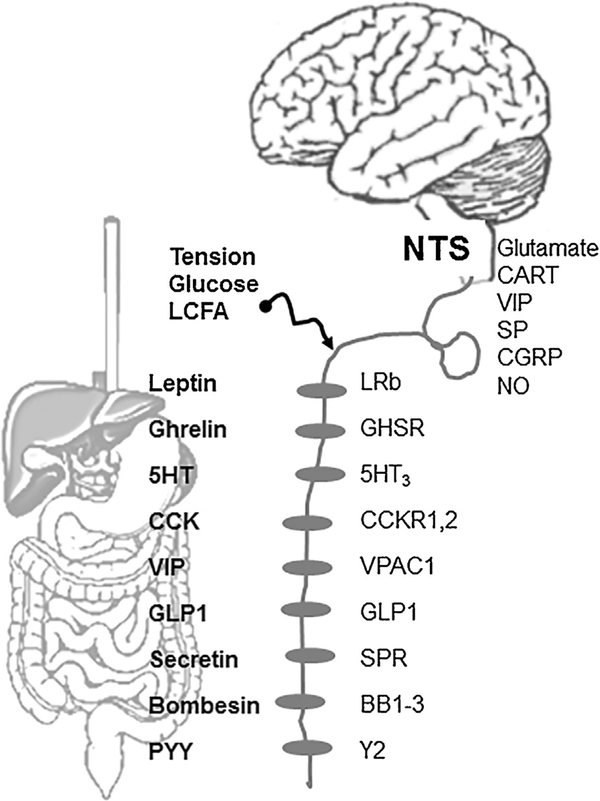
Fig. –
Vagal afferent signaling is regulated by complex neural, hormonal and mechanical signals. Nutrients trigger the release of gastrointestinal peptides that act on specific receptors on vagal afferents. Vagal afferents synapse with the second order neurons in the NTS by releasing a variety of neurotransmitters which act on higher centers to regulate gastrointestinal functions. 5HT3, serotonin receptor; BB1–3, bombesin receptors;CART, cocaine and amphetamine regulated transcript; CCK, cholecystokinin; CCK-1,2, cholecystokinin-1 and 2 type receptor; GHSR, growth hormone secretagogue receptor; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; GLP1, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; LCFA, long-chain fatty acid; LepR, leptin receptor; PYY, peptide YY; Y2-receptor; NO, nitric oxide; NTS, the nucleus of the solitarii tract; SP, substance P; SPR, secretin receptor; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide; VPAC1, receptor.