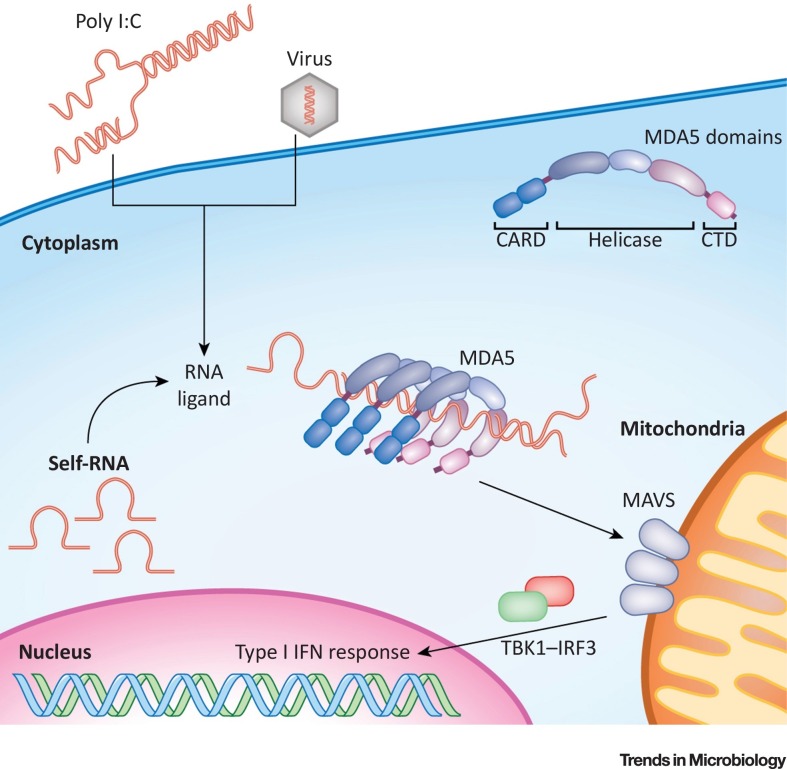
Figure 1.
Overview of the MDA5 Pathway. MDA5 comprises two N terminal CARD domains, a central helicase domain, and a C terminal domain (CTD). Both the helicase domain and the CTD are involved in RNA binding. MDA5 recognises synthetic RNAs, such as poly I:C, viral RNAs, and endogenous RNAs. Length and secondary structure are likely to be key determinants of MDA5 activation, which has been suggested to be mediated by multimerisation of the protein on RNA agonists. This results in the clustering of multiple CARD domains, which, in turn, allows the engagement of MAVS. Activation of this adaptor protein triggers a signalling cascade involving TBK1 and IRF3, leading to transcriptional induction of the genes encoding type I IFNs and other antiviral genes. CARD, caspase activation and recruitment domain; MAVS, mitochondrial antiviral signalling protein.