Fig. 1. Infection of PHA/IL-2 activated CD4+ T cells with NL4–3 LTR VSV-G pseudotyped pGBFM virus.
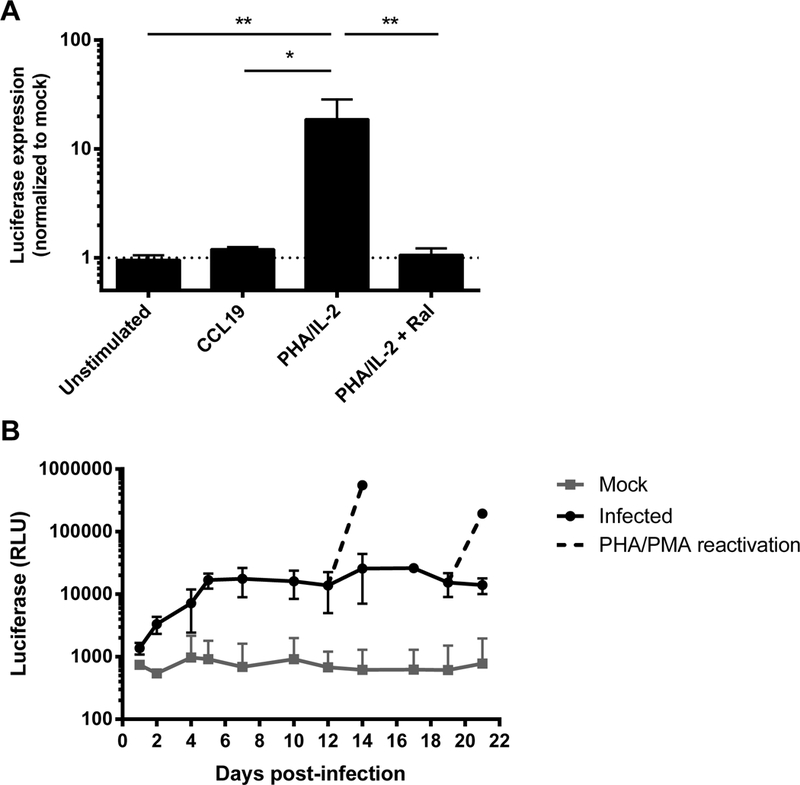
A. Primary resting CD4+ T cells isolated from healthy blood donors were left unstimulated, treated with CCL19, or were activated with PHA in the presence of IL-2 (with or without the integrase inhibitor raltegravir) for 48 hours prior to infection with NL4–3-LTR VSV-G pseudotyped pGBFM virus. Infection was quantified by measuring the level of luciferase produced on day 4. Mean ± SD values are shown from four independent experiments. * p<0.05 ** p<0.01. B. PHA-activated CD4+ T cells were infected as in (A) and the level of luciferase was measured every 1–3 days post-infection. On days 12 and 19 post-infection, cells in culture were further stimulated with PMA/PHA and luciferase measured two days after reactivation. The mean ± SD luciferase expression is shown from three independent donors.
