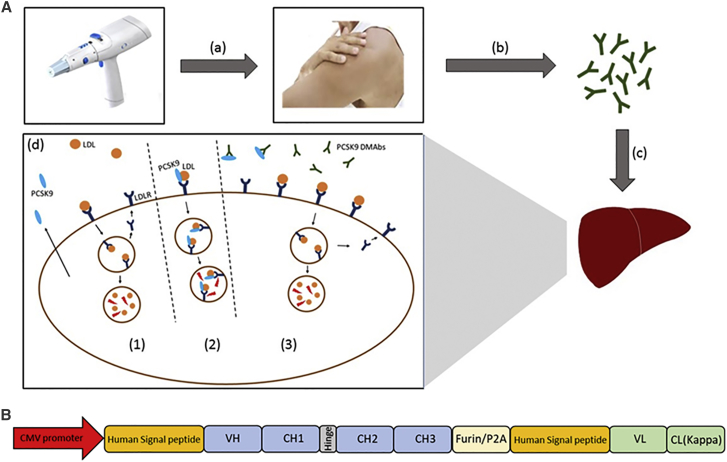
Figure 1.
Illustration of DMAb Approach
(A) Introduction of anti-PCSK9 DMAbs and mechanism of action. (a) In vivo electroporation device is used for intracellular delivery of anti-PCSK9 DMAb plasmids. (b) Intramuscular expression of DNA-encoded anti-PCSK9 mAbs and their subsequent release into the circulation. (c) Anti-PCSK9 DMAbs migrate to the liver where they bind and inhibit PCSK9. (d) Anti-PCSK9 DMAb mechanism of action. (1) LDL binding to LDLR results in uptake and degradation of LDL and recycling of LDLR. (2) PCSK9 binds LDLR, resulting in LDLR degradation. (3) Anti-PCSK9 DMAb inhibits PCSK9, allowing for increased LDLR recycling and display on the cell surface. (B) Schematic of the anti-PCSK9 DMAb bicistronic plasmid consisting of antibody heavy- and light-chain sequences separated by furin and P2A cleavage sites.