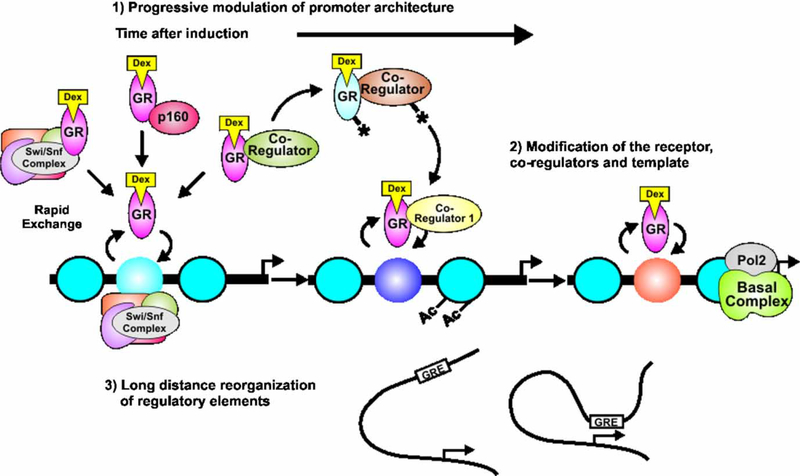
Figure 5.
The promoter progression model proposes an integrative view of fast and slow dynamics of receptors and cofactors at the promoter. Receptors and cofactors exchange rapidly with the template at response elements, allowing the regulatory sites to constantly sample receptor/cofactor complexes present in the nucleus. Promoter activity can be modulated in a time-dependent manner by multiple mechanisms, including (1) progressive modification of promoter chromatin structure, and (2) post-translational modification of factors involved in transcription initiation. Alteration in promoter modification and structure may include long distance architectural transfiguration to facilitate transcriptional initiation (3). GR, glucocorticoid receptor; Dex, dexamethasone; Pol II, RNA polymerase II; GRE, glucocorticoid responsive element; Ac, acetylation; p160, Figure 4, oactivator family.