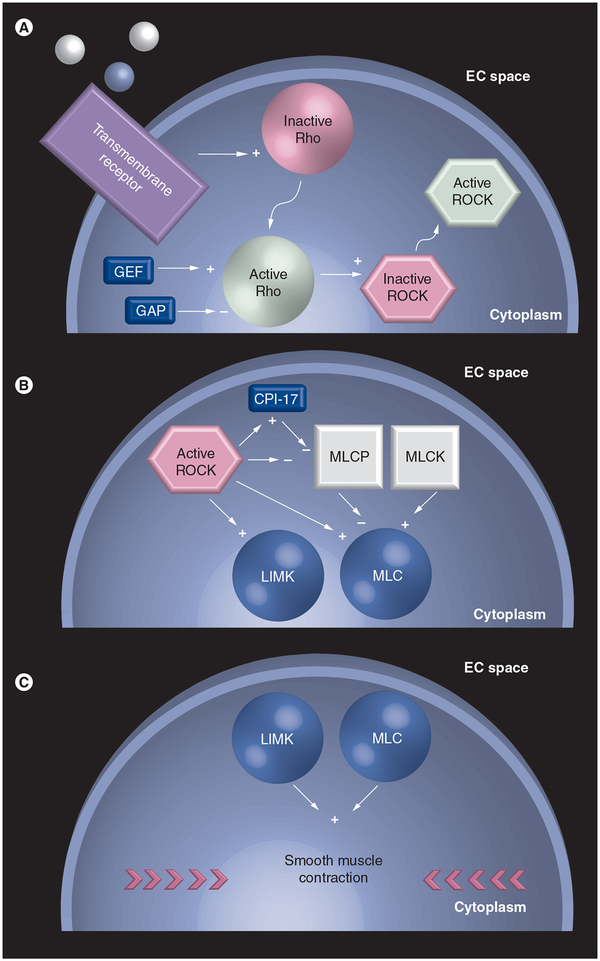
Figure 1. Rho GTPase signaling pathway.
Ligand binds transmembrane receptor, leading to Rho activation and translocation from the plasma membrane to the cytosol. (A) In the cytosol, Rho activates ROCK, which partially translocates to the plasma membrane. GEF and GAP provide additional regulation, activating and inhibiting Rho, respectively. ROCK activates LIMK and phosphorylates MLC. (B) The latter involves ROCK inhibition of MLCP, which dephosphorylates MLC. (C) Activation of LIMK and phosphorylation of MLC lead to smooth muscle contraction. Straight arrows with a plus indicate activation, straight arrows with a minus indicate inhibition, and bent arrows indicate translocation.
EC: Extracellular; GAP: GTPase-activating protein; GEF: Guanine nucleotide exchange factor; LIMK: LIM kinase; MLC: Myosin light chain; MLCK: Myosin light chain kinase; MLCP: Myosin light chain phosphatase; ROCK: Rho kinase.