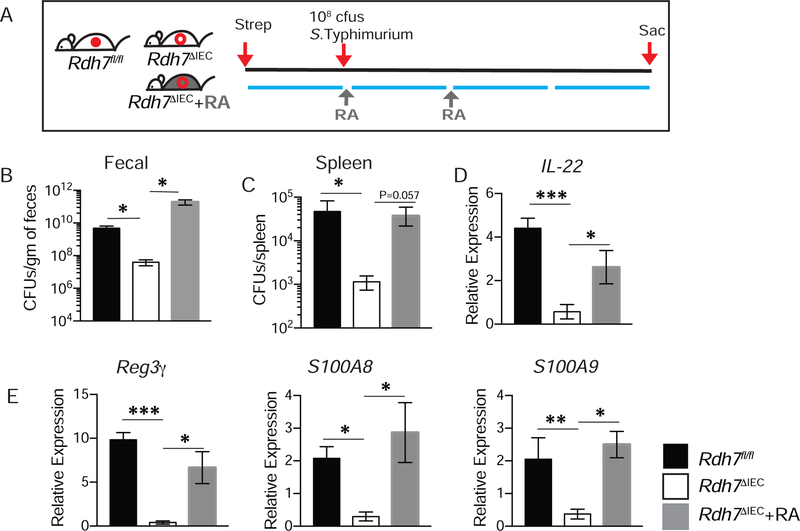
Figure 6. RA deficiency in Rdh7∆IEC mice is protective against pathogen colonization.
(A)Diagram illustrating S.Typhimurium infection and RA treatment timeline. 24 hours prior to infection, mice were treated with 20mg of streptomycin via oral gavage, followed by 108cfu/mL 24 post streptomycin. 250µg RA was administered twice intraperitoneally to Rdh7∆IEC. Mice were sacrificed 72 hours post infection.
(B) Quantification of S. Typhimurium bacterial burden in feces from streptomycin treated Rdh7fl/fl, Rdh7∆IEC and Rdh7∆IEC+RA mice at 72 hours post infection.
(C) S. Typhimurium burden in spleen after 72 hours post infection Rdh7fl/fl, Rdh7∆IEC and Rdh7∆IEC+RA streptomycin treated mice.
(D) mRNA quantification of Il-22 in the colon of Rdh7fl/fl, Rdh7∆IEC and Rdh7∆IEC+RA streptomycin treated mice 72 hours post infection with S. Typhimurium.
(E) mRNA quantification of IL-22 dependent antimicrobials, Reg3γ and calprotectin subunits S100A8 and S100A9 in the colon of Rdh7fl/fl, Rdh7∆IEC and Rdh7∆IEC+RA mice 72 hours post infection with S. Typhimurium.
All the mice used for this experiment were littermate controls that were co-housed before infection and housed separately after infection (N=6). Figures represent an individual experiment that was repeated four times. Error bar represent SEM. One-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001.
Also see Figure S5