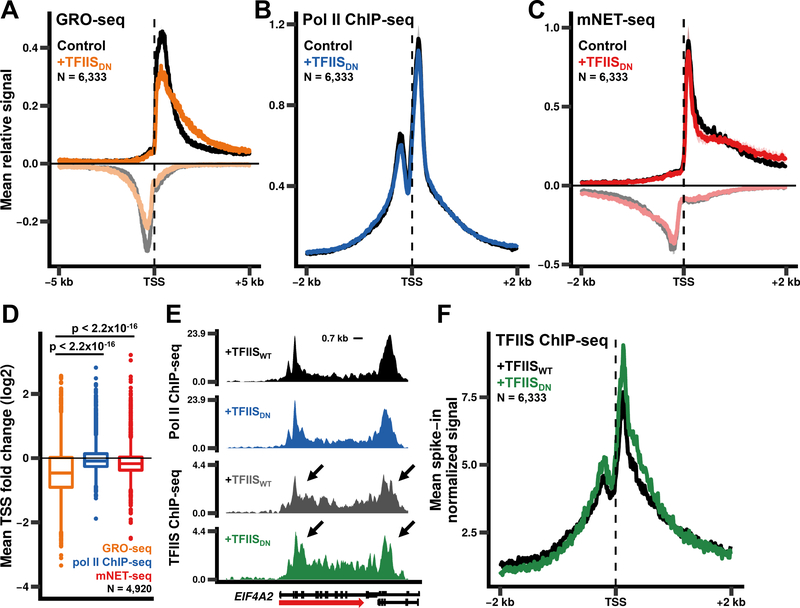
Figure 1. Pol II RNA cleavage activity promotes escape from 5’ pause sites.
(A)Expression of TFIISDN results in genome-wide loss of GRO-seq signal from promoter proximal regions. Metaplots of relative GRO-seq signals (10 bp bins) for genes >5 kb long and separated by >2 kb. The relative signal for each gene was calculated by dividing the signal in each bin by the total signal within the region plotted. The mean relative signal was calculated for each individual replicate. The mean relative signal was then averaged for the replicates with the shaded region representing the standard error of the means (SEM) for two biological replicates. Negative values correspond to anti-sense signal.
(B)Metaplots of relative anti-pol II ChIP-seq signals as in A. The mean and SEM for three biological replicates is shown.
(C)Metaplots of relative anti-pol II mNET-seq signals as in A. The mean and SEM for two biological replicates is shown.
(D)Fold change in GRO-seq, pol II ChIP-seq, and mNET-seq signals for the region from the TSS to +300 bp. The average fold change for two (GRO-seq, mNET-seq) or three (pol II ChIPseq) biological replicates is shown for genes >1 kb long and separated by >2 kb. p-values were calculated using the Welch two sample t-test with Bonferroni-Holm correction.
(E)TFIIS localizes to 5’ and 3’ ends of genes. Avi-TFIISWT and Avi-TFIISDN ChIP-seq signals for EIF4A2 normalized to a yeast spike-in (see Methods).
(F)WT TFIIS and TFIISDN associate with pol II at similar levels. Metaplots of Avi-TFIIS ChIPseq signals (10 bp bins) as in E.