Figure 1.
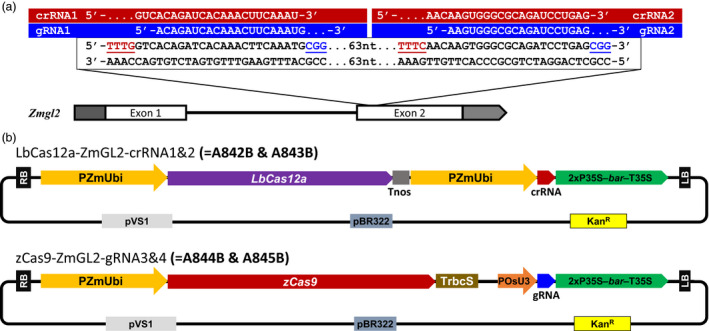
Comparison of Cas9 and Cas12a for genome editing in maize. (a) Cas9 and Cas12a target sequence in maize glossy2 (gl2), which is involved in epicuticular wax deposition in juvenile tissues. PAM sequences (TTTV for Cas12a and NGG for Cas9) were colored and underlined. (b) Schematic representations of the SpCas9 and LbCas12a constructs for Agrobacterium‐mediated maize transformation. RB, right border; LB, left border; PZmUbi, Zea mays Ubiquitin promoter; Tnos; nopaline synthase terminator; P35S, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA gene promoter; bar, bialaphos resistance gene; T35S, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S terminator; TrbcS, Pisum sativum rbcS E9 terminator, POsU3, Oryza sativa U3 small RNA promoter; pVS1, replication origin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa; pBR322, replication origin from pMB1; KanR, kanamycin resistance gene.
