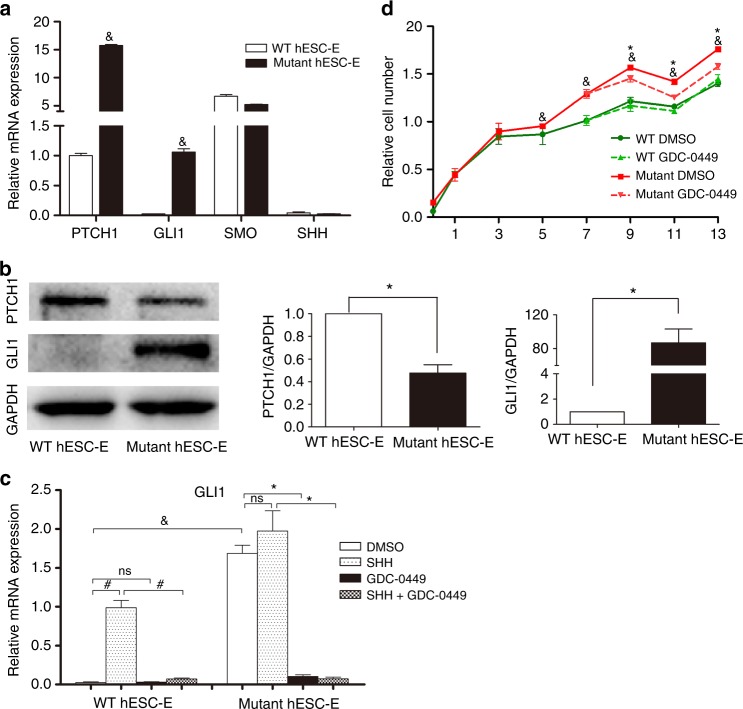
Fig. 4.
Status of sonic hedgehog (SHH) signalling and effects of GDC-0449 on wild-type (WT) and mutant human epithelial progenitor cells (hESC-Es) in vitro. a Real-time PCR demonstrating the mRNA levels of components of the SHH signalling pathway (PTCH1, GLI1, SMO and SHH) in WT (PTCH1+/+) and mutant (PTCH1R135X/+) hESC-Es. Data represent mean ± SD, n = 3 (&, mutant hESC-Es vs WT hESC-Es, p < 0.05). b Western blotting showed the protein levels of SHH pathway target genes (PTCH1 and GLI1) in WT and mutant hESC-Es. Expression of PTCH1 was reduced by half, and expression of GLI1 was significantly upregulated in mutant hESC-Es compared with WT hESC-Es (Data represent mean ± SD, n = 3, *P < 0.05). c The relative mRNA expression of GLI1 with exogenous SHH (1 μg•mL-1) and/or GDC-0449 (1 μmol•L-1) treatment for 24 h (&, #, *, P < 0.05; ns, P > 0.05). d GDC-0449 (1 μmol•L-1) was tested for its effects on the cell proliferation of WT and mutant hESC-Es. WT and mutant DMSO vehicle groups served as respective controls (&, mutant control group vs WT control group; *, mutant GDC-0449-treated group vs mutant DMSO control group; &, *, P < 0.05)