Figure 2.
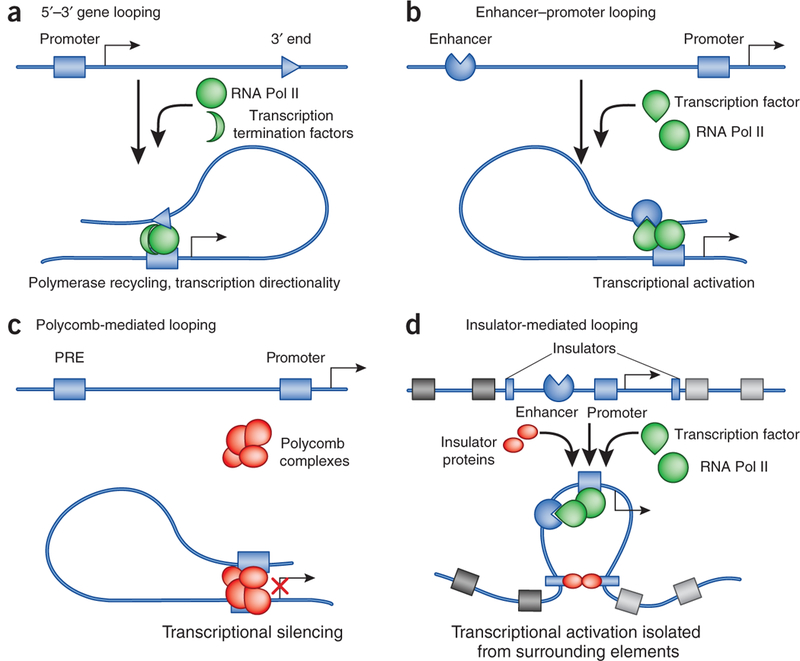
Four types of transcription regulatory chromatin loops. (a) Intragenic loops joining the 5’ and 3’ end of genes may allow recycling of RNA Pol II and facilitate maintenance of transcriptional directionality. (b) Enhancer- promoter loops—mediated by sequence-specific transcription factors, and possibly assisted by noncoding RNAs or by general DNA binding factors such as CTCF and cohesin—lead to transcriptional activation. (c) Loops between Polycomb-bound regions (PREs) and promoters prevent RNA Pol II recruitment and/or impair transcriptional elongation of promoter-bound RNA polymerases. (d) Insulator-mediated loops may segregate individual loci containing the coding part of the gene and its regulatory regions from the surrounding genome landscape with other regulatory elements.
