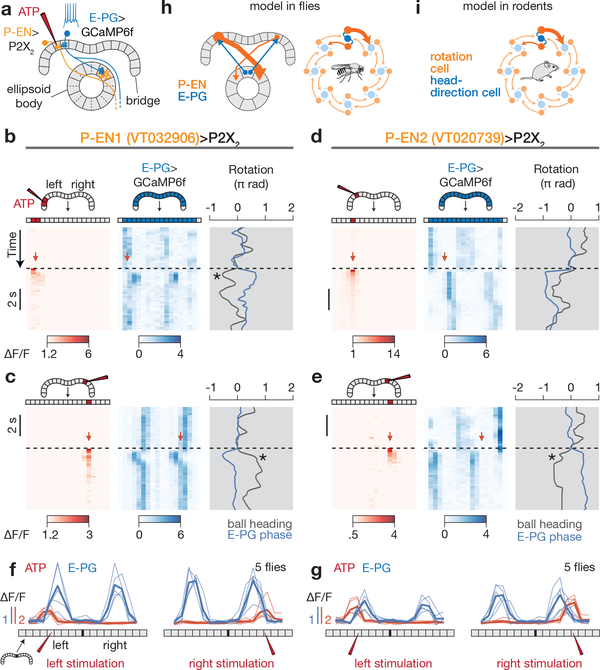
Figure 5 |. P-EN neurons medially excite E-PG neurons in the bridge, consistent with a model of neural integration.
a, Stimulating P2X2-expressing P-ENs in the bridge with ATP is expected to excite E-PGs in the medial neighboring glomerulus. b, Left, ATP (Alexa594) signal in the bridge; right, E-PG bridge activity while stimulating P-EN1 neurons in the left bridge. c, Same as b, except for stimulating P-EN1s in the right bridge. d, e, Same as b, c but for stimulating P-EN2 neurons. Asterisks highlight events when the fly turned following stimulation in a direction that would tend to return the E-PG phase to its pre-stimulus position. f, g, Phasenulled E-PG activity and ATP (Alexa594) signal after P-EN1 (f) or P-EN2 (g) stimulation. Thin lines represent the mean response in each fly. Thick lines represent the mean across flies. h, Summary model. P-EN and E-PG interactions projected onto a single ring. Only ellipsoid body tiles are represented for clarity. i, Model proposed in ref. 15 for rat head direction cells.