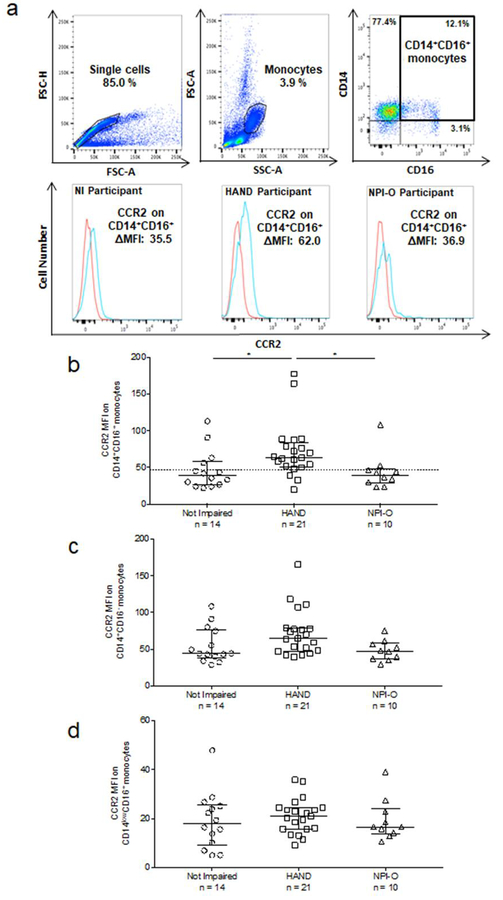
Fig. 1. HIV infected people with HAND have increased CCR2 on CD14+CD16+ monocytes.
. Surface CCR2 on three major monocyte subsets in PBMC from 45 subjects was determined by staining freshly isolated PBMC for human CD14, CD16, and CCR2, or with isotype matched control antibodies. Blood was drawn and PBMC isolated on the same day as neuropsychological assessment, which determined cognitive status. Cognitive status was determined as NI, HAND, or NPI-O. (a). Single cells were selected for analysis and forward- and side-scatter area (FSC-A and SSC-A) characteristics were used to determine monocyte gating. Monocyte subsets were then identified based on staining with isotype matched control, CD14 and CD16 antibodies. CD16 and the level of CD14 expression were used to gate for monocyte subsets, with high expression of both identifying CD14+CD16+ monocytes. CCR2 MFI was calculated by subtracting the MFI of the IgG2b isotype matched control antibody (red line) from the MFI of CCR2 (blue line) for each monocyte subset. (b). CCR2 MFI on CD14+CD16+ monocytes by cognitive status. (c). CCR2 MFI on CD14+CD16- monocytes by cognitive status. (d). CCR2 MFI on CD14lowCD16+ monocytes by cognitive status. Each data point is one individual subject, and data are represented as median ± IQR. Significance was determined by Kruskal Wallis test (p < 0.01) with multiple comparison’s post-hoc testing. * p < 0.05.