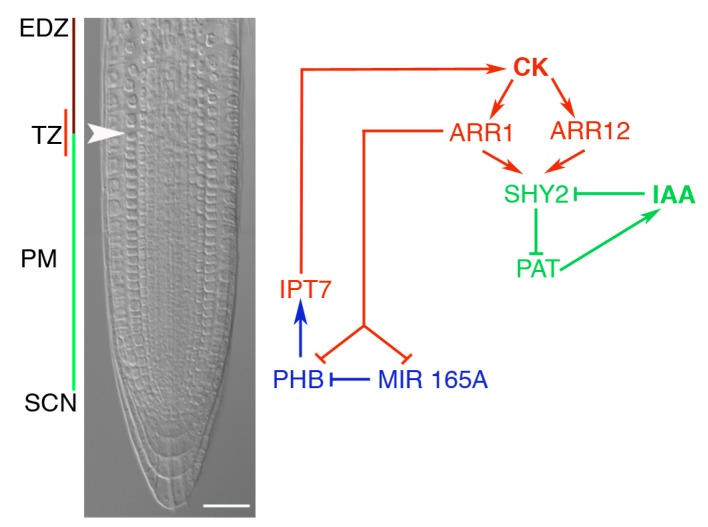
Figure 3.
Interplay between the HD-Zip III protein PHB and CKs in the regulation of root meristem size. DIC image of the Arabidopsis root tip with different developmental zones indicated, stem cell niche (SCN), proximal meristem (PM), transition zone (TZ), and elongation and differentiation zone (EDZ), together with a schematic representation of the molecular interactions involved in the determination of RAM size. PHB induces CK biosynthesis in the PM of the root; cytokinin is delivered to the transition zone where activates ARABIDOPSIS RESPONSE REGULATOR (ARR) 1. ARR1 represses the expression of PHB at the TZ, thus restricting PHB expression to the distal part of the PM. Remarkably, ARR1 also represses the transcription of MIR165A [135]. In addition, ARR1 induces the expression of SHY2, a CK primary target necessary and sufficient to promote cell differentiation at the TZ. White arrowhead indicates the TZ of the cortex tissue, placed at the boundary between the last meristematic cell and the first differentiating cell [137]. A color code has been used to indicate different pathways: CK pathway, red; IAA pathway, green; PHB/miR165, blue. Scale bar, 20 μm.