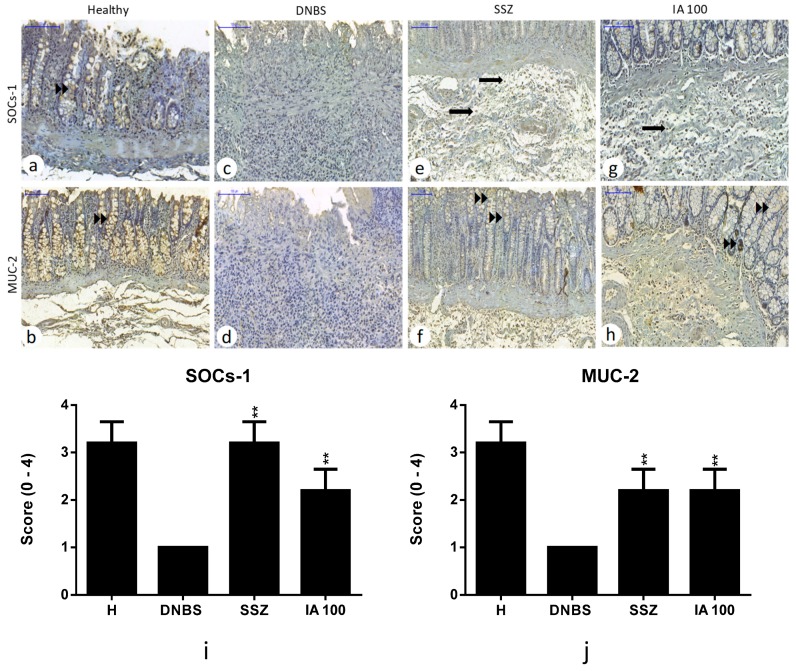
Figure 7.
Immunohistochemical analysis of the effect of 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg doses of I. asarifolia (IA) aqueous extract, and 250 mg/kg of sulfasalazine (SSZ) on intestinal colon mucosa in an experimental trial of acute colitis induced by 2,4-dinitrobenzene sulphonic acid (DNBS) in rats. Immunoreactivity was recognized by brownish staining in inflammatory cells, regardless of whether in the nucleus or cytoplasm. Healthy group (a,b) exhibiting moderate immunoreactivity for cytokine-1 signaling suppressor (SOCs-1) and mucin-2 (MUC-2) in the epithelium (►►). DNBS control (c,d), exhibiting no immunoreactivity for SOCs-1 and MUC-2. SSZ group with moderate immunoreactivity for SOCs-1 and discreet for MUC-2 (e,f). Group IA 100 mg/kg with mild immunoreactivity for SOCs-1 and MUC-2 (g,h). Inflammatory cells (➡). Immunoreactivity score (i,j). H, Healthy group; DNBS, DNBS group; SSZ, Sulfasalizine group; and 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg doses of IA. Expressed as mean ± SEM, (n = 5). The statistical differences ** p < 0.01 of the treatments are presented vs DNBS control (Scanner Panoramic Viewer, 100×).