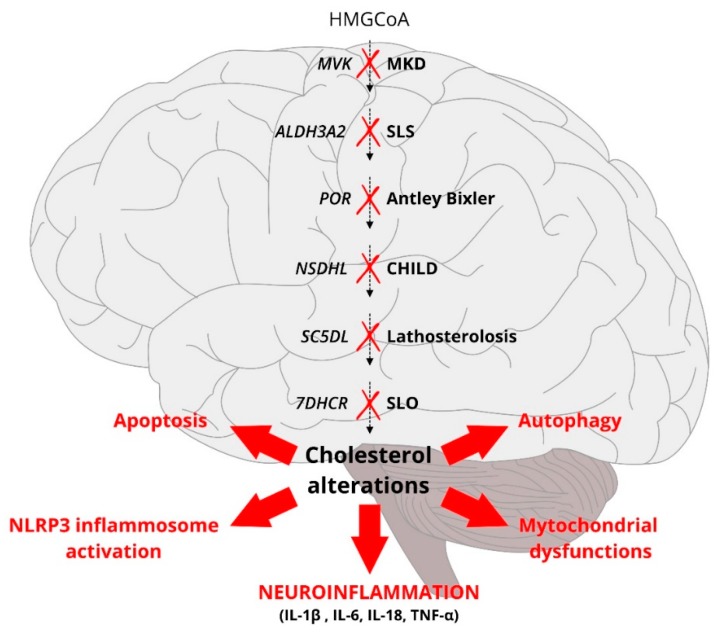
Figure 3.
Cholesterol biosynthesis deficiency syndromes. Schematic representation of the cholesterol pathway and some cholesterol–deficiency syndromes in response to different enzyme defects along the metabolic pathway (indicated with red crosses). Despite different specific causes, all these syndromes share the involvement of the central nervous system, where cholesterol reduction causes NLRP3-inflammosome activation, apoptosis, mitochondrial dysfunctions, autophagy and neuroinflammation with interleukin secretion (IL-1β, IL-18, IL-6 and TNF-α). HMG-CoA: 3-Hydroxy-3-MethylGlutaryl Co-enzyme; MVK: mevalotate kinase gene; MKD: Mevalonate Kinase Deficiency; ALDH3A2: Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 3 Family Member A2 gene; SLS: Sjogren-Larsson syndrome; POR: Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase gene; Antley-Bixler syndrome-like phenotype with disordered steroidogenesis; NSDHL: NAD(P) Dependent Steroid Dehydrogenase-Like gene; CHILD: congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosiform erythroderma and limb defects; SC5DL: Sterol-C5-Desaturase gene; Lathosterolosis; 7DHCR: 7-Dehydrocholesterol Reductase gene; SLO: Smith-Lemli-Opitz) syndrome; IL-1β: Interleukin 1 beta; IL-6: Interleukin 6; IL-18: Interleukin 18; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.