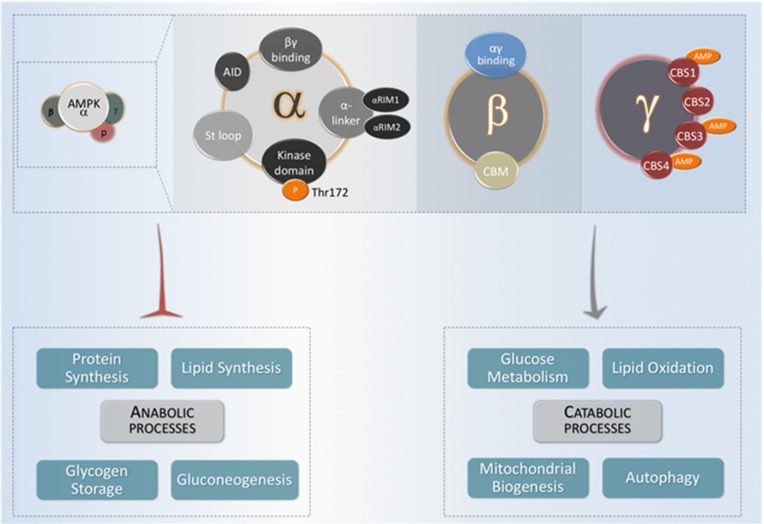
Figure 1.
The domain structure of AMPK (adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase) heterotrimer. Functional AMPK complexes consist of one catalytic and two regulatory subunits. When activated, AMPK acts by decreasing energy-consuming anabolic processes (lipid synthesis, glycogen storage, gluconeogenesis, and protein synthesis) and increasing energy-providing catabolic processes that provide ATP (glucose metabolism, lipid oxidation, mitochondrial biogenesis and autophagy).