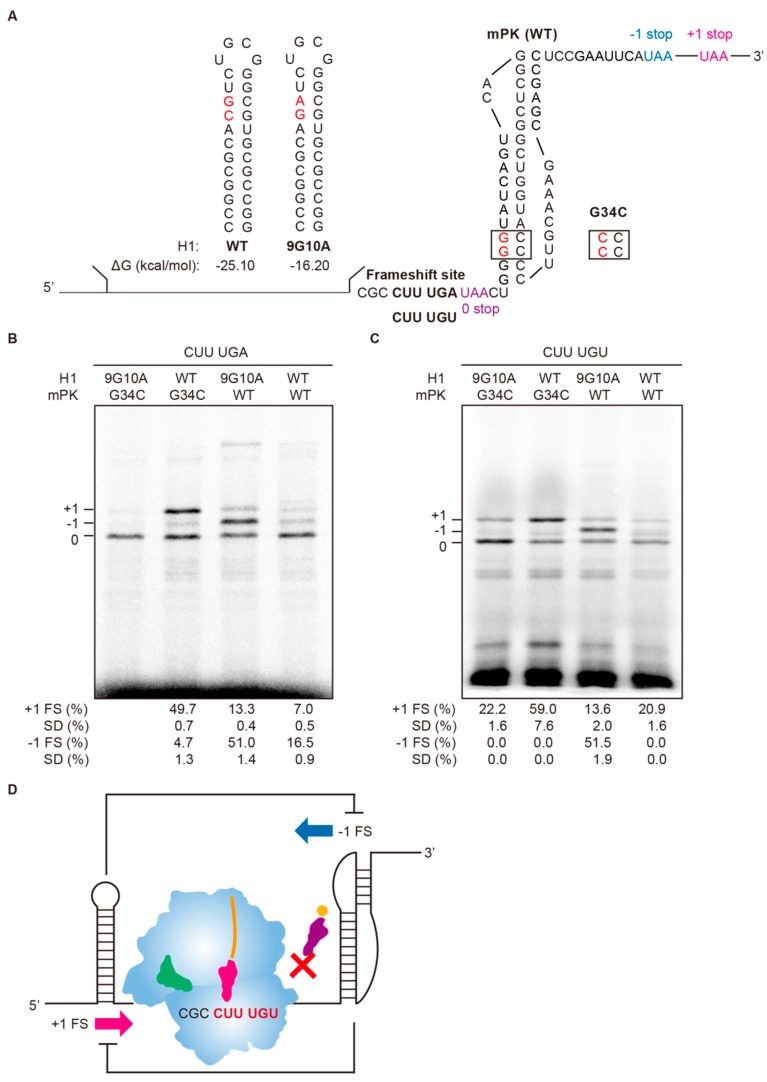
Figure 8.
Bidirectional reading-frame switch regulation by structures flanking an empty A-site ribosome. (A) Partial sequences for reporter constructs inserted with CUUUGA frameshifting site and flanking structures of different stabilities. The A-site codon is UGA for RF2 exclusion frameshifting assay and is followed by a UAA 0-frame stop codon (colored in purple) to facilitate proper translation termination. The −1 and +1 frame UAA stop codons (in colors) are located in the N-terminal region of Rluc ORF. Mutations to destabilize the upstream or downstream structures are shown in red. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of radioactivity-based frameshifting assay using constructs in (A) in the absence of RF2. (C) SDS-PAGE analysis of in vitro radioactivity-based frameshifting assay using constructs with CUUUGU frameshifting site and different flanking structures compared with those in (A). The experiments were performed under conditions with UGU as a hungry codon (Figure S6). Calculated −1 and +1 PRF efficiencies displayed are means ± SD of three independent experiments. (D) Scheme showing the opposite roles of flanking structures in bidirectional frameshifting regulation for an empty A-site ribosome.