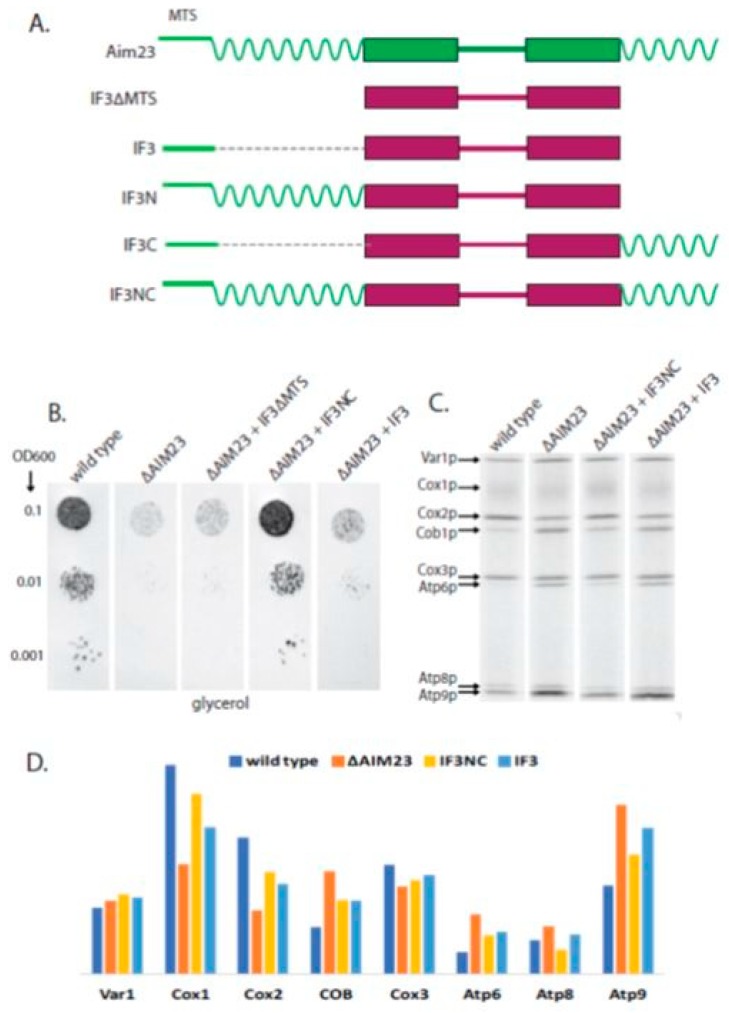
Figure 3.
Aim23p terminal extensions fused to bacterial IF3 restore the biological activity of the chimeric protein in yeast cells. (A) Scheme of the chimeric proteins (the names are indicated on the left). The designations of the main structural parts and their colors are the same as in Figure 1. (B) The plate with a glycerol-containing medium after 2 days of growth of the yeast strains indicated on the top. The ten-fold dilutions of the yeast suspensions were plated, starting from OD600 0.1 (indicated on the left). Wild-type and ∆AIM23: see Figure 2 legend. All other strains: D273-10B with the AIM23 genomic disruption supplemented with the corresponding mutant Aim23p version encoded by the plasmid. The experiment has been biologically repeated three times; the characteristic result is presented. (C) Separation of radioactively-labeled products of mitochondrial translation of the yeast strains indicated on the top. Cytosolic translation was inhibited by cycloheximide which was followed by adding of 35S-methionine incorporated exclusively in the mitochondrially-encoded proteins (for details, see Materials and Methods). The bands corresponding to all the eight individual proteins encoded in yeast mitochondria are visible; the proteins’ names are indicated on the left. (D) Estimated levels of the mitochondrially-encoded proteins (indicated on the bottom) after 15 min of labeling with 35S-methionine in the yeast strains indicated on the top.