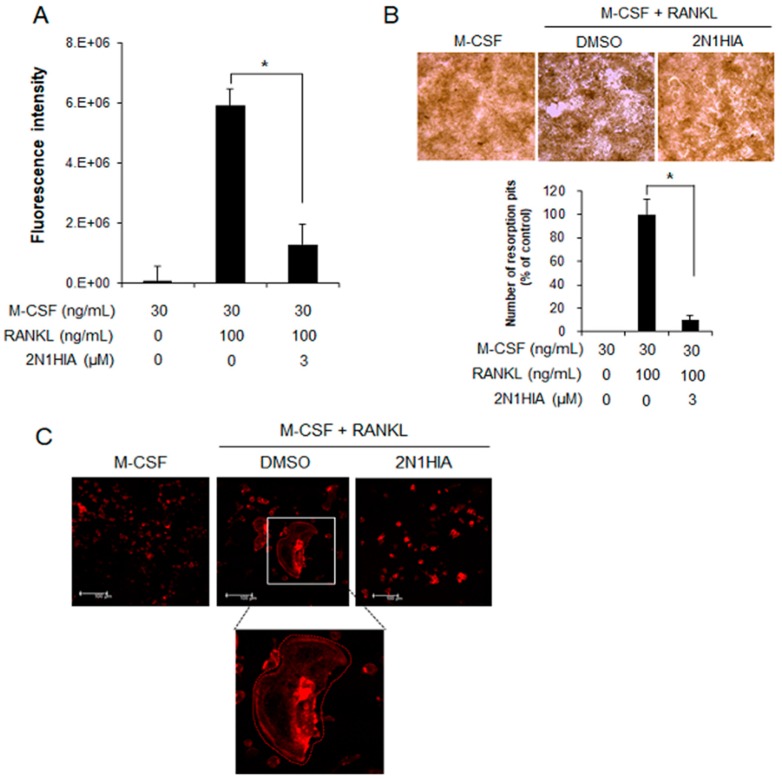
Figure 5.
Resorption activity of osteoclasts on bovine bone slices, with or without 2N1HIA. (A) The resorption index of osteoclasts differentiated from bone marrow with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (control) or treated with the 2N1HIA. Fluorescence intensity was measured at an excitation wavelength of 485 nm and an emission wavelength of 535 nm using a fluorometric plate reader. Data are expressed as percentages of the values of untreated cells (mean ± standard deviation, n = 3). (B) The visualized absorbed area with 2N1HIA treatment. Quantitative analysis of the pit area of the osteoclasts on calcium phosphate-coated plates, with and without 3 µM of 2N1HIA. The percentage area covered by resorption pits relative to untreated control was measured using the ImageJ software (version 1.41). A test was performed to evaluate significant differences. Three distinct sample pools were analyzed in a duplicate manner (n = 6). * p value < 0.05 is considered statistically significant compared the control. (C) Visualization of actin ring formation in RANKL-induced osteoclasts in the presence of 3 µM of 2N1HIA or the control, DMSO. The receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand-induced osteoclasts were cultured in the presence of 3 µM of 2N1HIA for four days. Cells were fixed and stained for actin rings as described in the Materials and Methods section. The data shown are representative of at least two independent experiments.